Configuring Grafana with Okta SSO Access
Configuring Grafana with Okta SSO Access
In this tutorial we will show you how to configure identity-based access to a self-hosted Grafana instance using Okta SSO, Teleport Enterprise and JWT tokens. In today’s technology landscape, with employees working remotely all across the globe, simple perimeter security is no longer good enough. Accessing infrastructure resources with long-lived credentials is a security nightmare waiting to happen. It’s not a question of if, but when, these credentials will eventually be leaked or stolen.
With Okta and Teleport Enterprise, however, you can configure access to applications like Grafana based on strict identity-based RBAC, so you know exactly who is accessing what on your network.
Key takeaways:
- How to host a Teleport-managed Grafana instance
- How to configure Okta SSO as an IDP provider for accessing Teleport
- How to map Teleport RBAC roles to Okta user groups
- Configure Teleport RBAC roles to adhere to the principle of least privilege
- Enable Passwordless access to your Grafana application
Grafana architecture
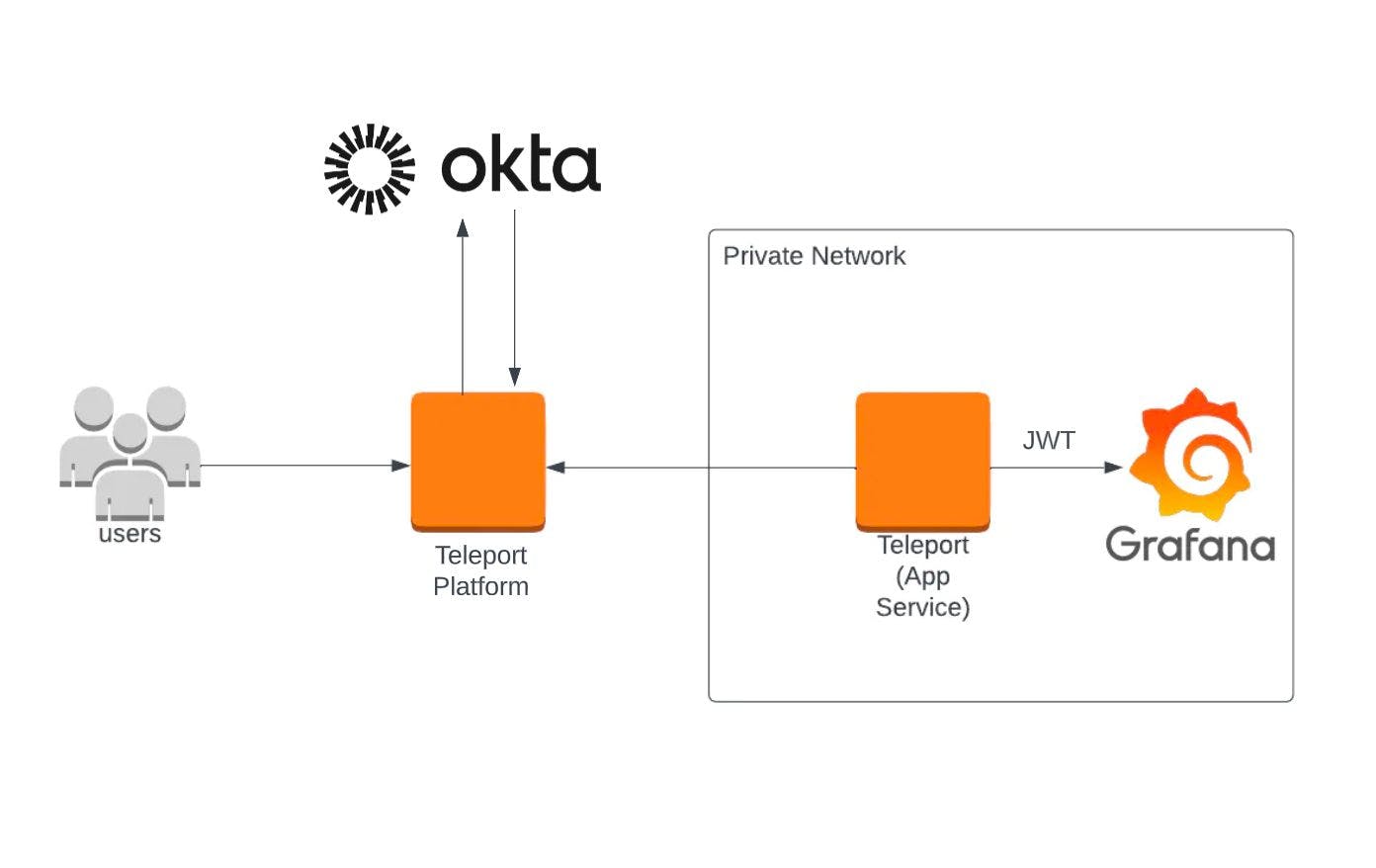
Above is a high-level diagram of the setup we’re going to be implementing. Instead of using a Grafana username and password to access our application, first users will authenticate with the Teleport platform using Okta SSO. In this case Teleport will act as a gateway and a proxy, gating access to your Grafana application, enforcing RBAC roles, all the while ensuring that all traffic between your users and the private application are fully encrypted.
The first step is to spin up a Grafana instance inside your Teleport cluster. You can follow the guide here in our docs to start up a containerized Grafana instance that will be managed by the Teleport cluster. As a prerequisite remember this requires Teleport Enterprise edition.
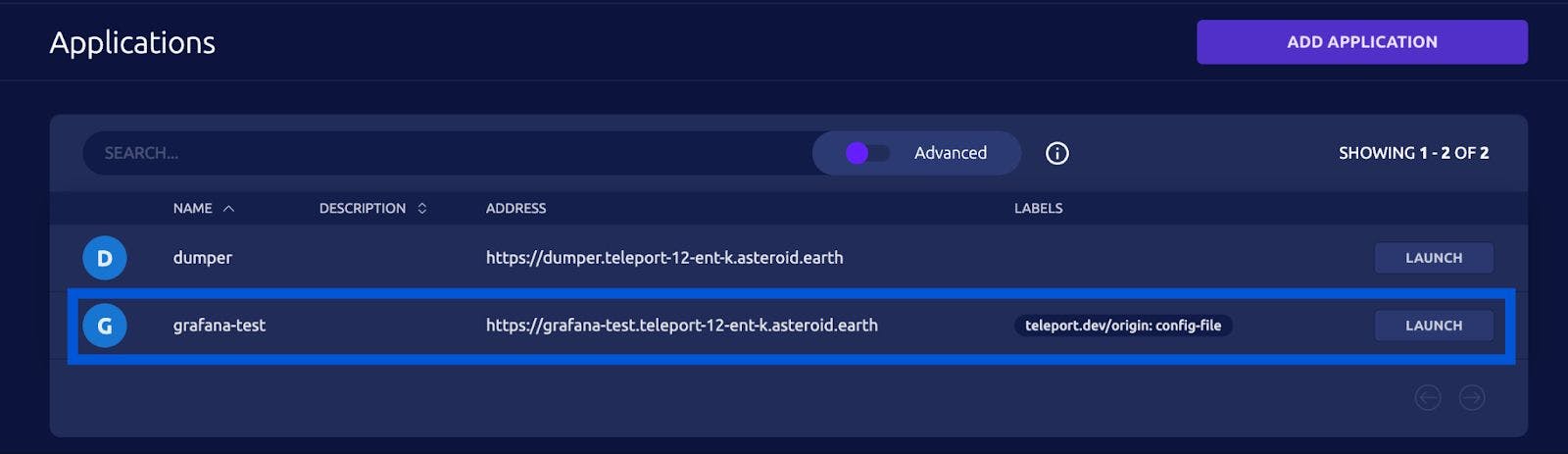
Once you have followed the steps listed in the docs, you should see your Grafana application listed here under the “Applications” Tab in your Teleport web UI. This will allow all users with the `access` role to access your Grafana application. We’re going to more finely tune these RBAC controls in the next sections.
Configuring Okta SSO Access for Teleport and Grafana
Now that we have our Grafana instance managed by our Teleport cluster, we’re going to configure Okta access for our cluster. We will also map our Okta groups to our Teleport roles allowing us to maintain a chain of custody for our users tied to their identities in Okta.
In order to configure Okta SSO to integrate with our Teleport cluster, please follow Steps 1 and 2 in our guide here.
Once you have created an application in the Okta dashboard to allow our Teleport cluster to access Okta as an IdP Provider, you should have two groups assigned to access Teleport:
We will map these two groups to separate Teleport RBAC roles ensuring that we are following the principle of least privilege. This mapping will ensure that our users only have the minimum permissions that they need in order to do their jobs.
Creating the Teleport SAML connector
First update the auth_service field in your Teleport configuration file, which is located by default at `/etc/teleport.yaml`.
```
auth_service:
authentication:
type: saml
```
Then restart the Teleport daemon.
Once Teleport has been updated with the new SAML authentication scheme, we’re going to add a SAML connector Teleport resource.
Define a SAML connector resource in a local file named `okta-connector.yaml`.
```
# This connector can be used for SAML endpoints like Okta
kind: saml
version: v2
metadata:
# the name of the connector
name: okta
spec:
display: Okta
# cluster-url is the address the cluster UI is reachable at.
acs: https://<cluster-url>/v1/webapi/saml/acs/new_saml_connector
allow_idp_initiated: false
attributes_to_roles:
- name: groups
value: okta-admin
roles:
- editor
- name: groups
value: okta-dev
roles:
- grafana-dev
# Provides a path to the IdP metadata.
entity_descriptor_url: https://example.okta.com/app/your-app-id/sso/saml/metadata
```
Make sure to replace <cluster-url> with the publicly accessible domain of your Teleport cluster.
Also replace the value of `entity_descriptor_url` with the path you copy following this step from the previous guide.
Notice the `attributes_to_roles` section. This is where we map the attributes in the okta-roles to our Teleport RBAC roles. For the `okta-admin` okta role attribute, we map it to our Teleport `editor` role. This will allow users in this Okta group to edit roles and resources in our Teleport cluster.
The `okta-dev` group, on the other hand, only allows access to our Teleport `grafana-dev` role which we’ll create in the next section. This role will be more restrictive and only allow access to our Grafana dashboard.
Once you have defined this connector resource in the yaml file, create it using the `tctl` tool:
`$ tctl create okta-connector.yaml`
Creating our grafana-dev Teleport role
Next we’ll create our `grafana-dev` role to pull in external information from Okta.
Teleport administrators can configure roles to allow or deny users' access to applications with specific labels using `app_labels` property.
As an example, here is how you can configure your Grafana application with a “metrics” label.
```
apps:
- name: "grafana"
uri: "http://localhost:3000"
# Static labels.
labels:
group: "metrics"
commands:
- name: "arch"
command: ["uname", "-p"]
period: 1m0s
```
We’ll use this metrics label to assign our `grafana-dev` role access to applications in the `metrics` group.
Create the local file `grafana-dev-role.yaml`.
```
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: grafana-dev
spec:
options:
max_session_ttl: 24h
allow:
logins: [ "{{email.local(external.username)}}", ubuntu ]
app_labels:
group: "metrics"
```
Notice the `{{external.username}}` login. It configures Teleport to look at the "username" Okta claim and use that field as an allowed login for each user. This example uses email as the username format. The `email.local(external.username)` function call will remove the `@domain` and leave the username prefix.
Use `tctl` to create this role in the Teleport Auth Service:
`$ tctl create dev.yaml`
Configuring JWT authentication to Grafana
Now that we have Okta SSO as our identity provider — configured for our Teleport cluster — and now that we have successfully mapped our Okta user groups to Teleport roles, the final step is to pass the JWT token attributed to our user session to our Grafana application. This will allow a single sign-on flow for Teleport users accessing our Grafana instance.
In your `grafana.ini` configuration file, located on the node where you are hosting your Grafana application, overwrite the `[auth.basic]` section and the `[auth.jwt]` section with the following values:
```
[auth.basic]
enabled = false
[auth.jwt]
disable_login_form = true
enabled = true
header_name = Teleport-Jwt-Assertion
email_claim = sub
username_claim = sub
auto_sign_up = true
```
This will allow Grafana to receive the JWT token attributed to the user-section, allowing passwordless access into your Grafana application.
Secure and audited identity-based Grafana access
Now that we have successfully configured Okta SSO authentication to our Teleport cluster, mapped our Okta roles to our Teleport roles, and also configured JWT authentication for our Grafana instance, our users now are able to access Grafana based on the RBAC policies we have in place. This allows us to centralize all of our access to one location, cutting down on silos, reducing overhead and enforcing best security practices across the organization.
- For further reading on configuring JWT authentication for Grafana, please check out their documentation here.
- For further information and troubleshooting help for Okta SSO authentication for Teleport, please check out our guide here.
Not a Teleport Enterprise user quite yet? Request a free Enterprise Cloud trial today and get started with identity-native, zero-trust, secure application access!
