
Teleport
Amazon Athena Access
- Version 17.x
- Version 16.x
- Version 15.x
- Version 14.x
- Older Versions
You can set up secure access to Amazon Athena using Teleport's support for the AWS CLI and Console.
This guide will help you to:
- Install the Teleport Application Service.
- Set up AWS CLI and Console access.
- Connect to your Athena databases.
Prerequisites
- AWS account with Athena databases.
- IAM permissions to create IAM roles.
awsCommand Line Interface (CLI) tool installed in PATH.- A host, e.g., an EC2 instance, where you will run the Teleport Application Service.
-
A running Teleport cluster version 16.1.0 or above. If you want to get started with Teleport, sign up for a free trial or set up a demo environment.
-
The
tctladmin tool andtshclient tool.Visit Installation for instructions on downloading
tctlandtsh.
- To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials.tctlis supported on macOS and Linux machines. For example:If you can connect to the cluster and run thetsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=[email protected]tctl statusCluster teleport.example.com
Version 16.1.0
CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678
tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions.
If you have not yet deployed the Auth Service and Proxy Service, you should follow one of our getting started guides or try our Teleport application access interactive learning track.
We will assume your Teleport cluster is accessible at teleport.example.com and *.teleport.example.com. You can substitute the address of your Teleport Proxy Service. (For Teleport Cloud customers, this will be similar to mytenant.teleport.sh.)
Teleport assigns a subdomain to each application you configure for Application
Access. For example, if you enroll Grafana as a resource, Teleport assigns the resource
to the grafana.teleport.example.com subdomain.
If you host the Teleport cluster on your own network, you should update your DNS configuration to account for application subdomains. You can update DNS in one of two ways:
- Create a single DNS address (A) or canonical name (CNAME) record using wildcard substitution
for the subdomain name. For example, create a DNS record with the name
*.teleport.example.com. - Create a separate DNS address (A) or canonical name (CNAME) record for each application subdomain.
Modifying DNS ensures that the certificate authority—for example, Let's Encrypt—can issue a certificate for each subdomain and that clients can verify Teleport hosts regardless of the application they are accessing.
If you use the Teleport cloud platform, no DNS updates are needed because your Teleport cluster automatically provides the subdomains and signed TLS certificates for your applications under your tenant address.
Step 1/5. Create an IAM role for Athena access
Create an IAM role that provides access to your Athena resources. Teleport Application Service will assume this IAM role on behalf of the Teleport user that accesses these Athena resources.
There are several methods to create an IAM role:
Visit the Roles page of the AWS Console, then press "Create Role".
Select the "AWS account" option, which creates a default trust policy to allow other entities in this account to assume this role:
Press "Next". Find the AWS-managed policy AmazonAthenaFullAccess and then select the policy:
Press "Next". Enter role name ExampleTeleportAthenaRole and press "Create role":
Create a file with the following trust policy. Replace aws-account-id with your AWS Account ID:
cat > trust-relationship.json <<EOF{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::aws-account-id:root" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole" } ]}EOF
Create an IAM role with name ExampleTeleportAthenaRole:
aws iam create-role --role-name ExampleTeleportAthenaRole --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-relationship.json
Attach managed policy AmazonAthenaFullAccess to the role:
aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name ExampleTeleportAthenaRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonAthenaFullAccess
Add the following resources to your Terraform deployment. Replace aws-account-id with your AWS Account ID:
cat > teleport_iam_role_ExampleTeleportAthenaRole.tf <<EOFresource "aws_iam_role" "teleport-ExampleTeleportAthenaRole" { name = "ExampleTeleportAthenaRole" assume_role_policy = jsonencode({ Version = "2012-10-17" Statement = [ { Effect = "Allow" Principal = { AWS = "arn:aws:iam::aws-account-id:root" } Action = "sts:AssumeRole" }, ] })}resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "teleport-ExampleTeleportAthenaRole-AmazonAthenaFullAccess" { role = aws_iam_role.teleport-ExampleTeleportAthenaRole.name policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonAthenaFullAccess"}EOF
Then terraform apply.
AmazonAthenaFullAccess may provide too much access for your intentions. To
use a different IAM policy to reduce permissions, see Identity and access
management in
Athena
for more details.
Step 2/5. Configure the Teleport IAM role mapping
Give your Teleport users permissions to assume IAM roles in your Teleport cluster.
You can do this by creating a Teleport role with the aws_role_arns field
listing the IAM role ARN created in the previous step. Create a file called
aws-athena-access.yaml with the following content:
cat > aws-athena-access.yaml <<EOFkind: roleversion: v5metadata: name: aws-athena-accessspec: allow: app_labels: '*': '*' aws_role_arns: - arn:aws:iam::aws-account-id:role/ExampleTeleportAthenaRoleEOF
Remember to replace aws-account-id with your AWS Account ID.
The aws_role_arns field supports template variables so they can be populated
dynamically based on your users' identity provider attributes. Here are some
examples:
Use {{internal.aws_role_arns}} in the role definition:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: aws-athena-access
spec:
allow:
app_labels:
'*': '*'
aws_role_arns: ['{{internal.aws_role_arns}}']
Then specify the IAM roles through user traits:
kind: user
version: v2
metadata:
name: alice
spec:
roles: ['aws-athena-access']
traits:
aws_role_arns: ['arn:aws:iam:123456789000:role/role_for_alice']
---
kind: user
version: v2
metadata:
name: bob
spec:
roles: ['aws-athena-access']
traits:
aws_role_arns: ['arn:aws:iam:123456789000:role/role_for_bob']
Let's assume that an IAM role has been created for each Teleport user, and the name of the IAM role corresponds to their Email addresses without the Email domain suffix.
Then aws_role_arns can be templated with external.email:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: aws-athena-access
spec:
allow:
app_labels:
'*': '*'
aws_role_arns: ['arn:aws:iam:123456789000:role/{{email.local(external.email)}}']
See Role Templates for details.
Create the new role:
tctl create -f aws-athena-access.yaml
Assign the aws-athena-access role to your Teleport user by running the appropriate
commands for your authentication provider:
-
Retrieve your local user's roles as a comma-separated list:
ROLES=$(tsh status -f json | jq -r '.active.roles | join(",")') -
Edit your local user to add the new role:
tctl users update $(tsh status -f json | jq -r '.active.username') \ --set-roles "${ROLES?},aws-athena-access" -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
githubauthentication connector:tctl get github/github --with-secrets > github.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto thegithub.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the github.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
github.yaml, addingaws-athena-accessto theteams_to_rolessection.The team you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the team must include your user account and should be the smallest team possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
teams_to_roles: - organization: octocats team: admins roles: - access + - aws-athena-access -
Apply your changes:
tctl create -f github.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
samlconfiguration resource:tctl get --with-secrets saml/mysaml > saml.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto thesaml.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the saml.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
saml.yaml, addingaws-athena-accessto theattributes_to_rolessection.The attribute you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the group must include your user account and should be the smallest group possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
attributes_to_roles: - name: "groups" value: "my-group" roles: - access + - aws-athena-access -
Apply your changes:
tctl create -f saml.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
oidcconfiguration resource:tctl get oidc/myoidc --with-secrets > oidc.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto theoidc.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the oidc.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
oidc.yaml, addingaws-athena-accessto theclaims_to_rolessection.The claim you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the group must include your user account and should be the smallest group possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
claims_to_roles: - name: "groups" value: "my-group" roles: - access + - aws-athena-access -
Apply your changes:
tctl create -f oidc.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
Step 3/5. Install the Teleport Application Service
Generate a token
A join token is required to authorize a Teleport Application Service instance to join the cluster. Generate a short-lived join token and save the output of the command:
tctl tokens add \ --type=app \ --app-name=aws \ --app-uri=https://console.aws.amazon.com/console/home
On the host where you will run the Teleport Application Service, copy the token
to a file called /tmp/token.
Replace https://console.aws.amazon.com with
https://console.amazonaws-us-gov.com for AWS GovCloud (US) regions or
https://console.amazonaws.cn for AWS China regions.
Install and start Teleport
Install Teleport on the host where you will run the Teleport Application Service. See our Installation page for options besides Linux servers.
Install Teleport on your Linux server:
-
Assign edition to one of the following, depending on your Teleport edition:
Edition Value Teleport Enterprise Cloud cloudTeleport Enterprise (Self-Hosted) enterpriseTeleport Community Edition oss -
Get the version of Teleport to install. If you have automatic agent updates enabled in your cluster, query the latest Teleport version that is compatible with the updater:
TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.comTELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"Otherwise, get the version of your Teleport cluster:
TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.comTELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/ping | jq -r '.server_version')" -
Install Teleport on your Linux server:
curl https://goteleport.com/static/install.sh | bash -s ${TELEPORT_VERSION} editionThe installation script detects the package manager on your Linux server and uses it to install Teleport binaries. To customize your installation, learn about the Teleport package repositories in the installation guide.
Edit the Teleport configuration file (/etc/teleport.yaml) to include the
following information, adjusting the value of proxy_server to specify the host
and port of your Teleport Proxy Service:
version: v3
teleport:
join_params:
token_name: "/tmp/token"
method: token
proxy_server: "teleport.example.com:443"
auth_service:
enabled: off
proxy_service:
enabled: off
ssh_service:
enabled: off
app_service:
enabled: true
apps:
- name: aws
uri: https://console.aws.amazon.com/home/home
Grant the Teleport Application Service access to credentials that it can use to authenticate to AWS. If you are running the Teleport Application Service on an EC2 instance, you may use the EC2 Instance Metadata Service method. Otherwise, you must use environment variables:
Teleport will detect when it is running on an EC2 instance and use the Instance Metadata Service to fetch credentials.
The EC2 instance should be configured to use an EC2 instance profile. For more information, see: Using Instance Profiles.
Teleport's built-in AWS client reads credentials from the following environment variables:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_DEFAULT_REGION
When you start the Teleport Application Service, the service reads environment variables from a
file at the path /etc/default/teleport. Obtain these credentials from your
organization. Ensure that /etc/default/teleport has the following content,
replacing the values of each variable:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=00000000000000000000
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=<YOUR_REGION>
Teleport's AWS client loads credentials from different sources in the following order:
- Environment Variables
- Shared credentials file
- Shared configuration file (Teleport always enables shared configuration)
- EC2 Instance Metadata (credentials only)
While you can provide AWS credentials via a shared credentials file or shared
configuration file, you will need to run the Teleport Application Service with the AWS_PROFILE
environment variable assigned to the name of your profile of choice.
If you have a specific use case that the instructions above do not account for, consult the documentation for the AWS SDK for Go for a detailed description of credential loading behavior.
Configure the Teleport Application Service to start automatically when the host boots up by creating a systemd service for it. The instructions depend on how you installed the Teleport Application Service.
On the host where you will run the Teleport Application Service, enable and start Teleport:
sudo systemctl enable teleportsudo systemctl start teleport
On the host where you will run the Teleport Application Service, create a systemd service configuration for Teleport, enable the Teleport service, and start Teleport:
sudo teleport install systemd -o /etc/systemd/system/teleport.servicesudo systemctl enable teleportsudo systemctl start teleport
You can check the status of the Teleport Application Service with systemctl status teleport
and view its logs with journalctl -fu teleport.
For non-standard AWS regions such as AWS GovCloud (US) regions and AWS China
regions, please set the corresponding region in the AWS_REGION environment
variable or in the AWS credentials file so that the Application Service can use
the correct STS endpoint.
Step 4/5. Give Teleport permissions to assume roles
Next, attach the following policy to the IAM role or IAM user the Teleport Application Service instance is using, which allows the Application Service to assume the IAM roles:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
You can make the policy more strict by providing specific IAM role resource ARNs in the "Resource" field instead of using a wildcard.
Step 5/5. Connect
Once the Application Service has started and joined the cluster, you can start connecting to your Athena database.
Using AWS Management Console
Log in to the Teleport Web UI at https://teleport.example.com (replace with
your Proxy Service's public address).
Navigate to the Applications tab in your Teleport cluster's control panel and click on the Launch button for the AWS application. This will bring up an IAM role selector:
Click on the role ExampleTeleportAthenaRole and you will get redirected to the AWS
Management Console, signed in with the selected role.
In the console's top-right corner, you should see that you're logged in through
federated login and the name of your assumed IAM role is
ExampleTeleportAthenaRole/<teleport-username> where the session name is your Teleport username.
Using AWS CLI
Log into the previously configured AWS app on your desktop:
tsh apps login --aws-role ExampleTeleportAthenaRole awsLogged into AWS app aws. Example AWS CLI command:tsh aws s3 ls
The --aws-role flag allows you to specify the AWS IAM role to assume when
accessing the AWS API. You can either provide a role name like --aws-role ExampleTeleportDynamoDBRole or a full role ARN like
arn:aws:iam::123456789000:role/ExampleTeleportAthenaRole.
Now you can use the tsh aws command like the native aws command-line tool:
tsh aws athena list-work-groups
To log out of the aws application and remove credentials:
tsh apps logout aws
Using other Athena applications
First, log into the previously configured AWS app if you haven't already done so:
tsh apps login --aws-role ExampleTeleportAthenaRole aws
Connect to Athena with the ODBC or JDBC driver:
Start a local HTTPS proxy:
tsh proxy aws --port 8443 --format athena-odbcStarted AWS proxy on http://127.0.0.1:8443.
Set the following properties for the Athena ODBC data source:[Teleport AWS Athena Access]AuthenticationType = IAM CredentialsUID = abcd1234-this-is-an-examplePWD = zyxw9876-this-is-an-exampleUseProxy = 1;ProxyScheme = http;ProxyHost = 127.0.0.1;ProxyPort = 8443;TrustedCerts = <local-ca-bundle-path>
Here is a sample connection string using the above credentials and proxy settings:DRIVER=Simba Amazon Athena ODBC Connector;AuthenticationType=IAM Credentials;UID=abcd1234-this-is-an-example;PWD=zyxw9876-this-is-an-example;UseProxy=1;ProxyScheme=http;ProxyHost=127.0.0.1;ProxyPort=8443;TrustedCerts=<local-ca-bundle-path>;AWSRegion=<region>;Workgroup=<workgroup>
Use the provided connection string in your Athena application with ODBC driver.
Start a local HTTPS proxy:
tsh proxy aws --port 8443 --format athena-jdbcStarted AWS proxy on http://127.0.0.1:8443.
First, add the following certificate to your keystore:<local-ca-bundle-path>
For example, to import the certificate using "keytool":keytool -noprompt -importcert -alias teleport-aws -file <local-ca-bundle-path> -keystore <keystore>
Then, set the following properties in the JDBC connection URL:User = abcd1234-this-is-an-examplePassword = zyxw9876-this-is-an-exampleProxyHost = 127.0.0.1;ProxyPort = 8443;
Here is a sample JDBC connection URL using the above credentials and proxy settings:jdbc:awsathena://User=abcd1234-this-is-an-example;Password=zyxw9876-this-is-an-example;ProxyHost=127.0.0.1;ProxyPort=8443;AwsRegion=<region>;Workgroup=<workgroup>
Follow the printed instructions to add the local certificate to your Java Keystore. The default Java Keystore is usually located at:
$ ls $(java -XshowSettings:properties -version 2>&1 | grep 'java.home' | awk '{print $3}')/lib/security/cacerts
Then use the provided JDBC connection URL for your Athena application with JDBC driver.
Start a local HTTPS proxy:
tsh proxy aws --port 8443 --format athena-jdbcStarted AWS proxy on http://127.0.0.1:8443.
First, add the following certificate to your keystore:<local-ca-bundle-path>
For example, to import the certificate using "keytool":keytool -noprompt -importcert -alias teleport-aws -file <local-ca-bundle-path> -keystore <keystore>
Then, set the following properties in the JDBC connection URL:User = abcd1234-this-is-an-examplePassword = zyxw9876-this-is-an-exampleProxyHost = 127.0.0.1;ProxyPort = 8443;
Here is a sample JDBC connection URL using the above credentials and proxy settings:jdbc:awsathena://User=abcd1234-this-is-an-example;Password=zyxw9876-this-is-an-example;ProxyHost=127.0.0.1;ProxyPort=8443;AwsRegion=<region>;Workgroup=<workgroup>
Note that DBeaver uses its own Java Keystore instead of the default one. For
example, on macOS, the Keystore location is
/Applications/DBeaver.app/Contents/Eclipse/jre/Contents/Home/lib/security/cacerts.
Follow Importing CA Certificates into
DBeaver
to setup the Keystore for DBeaver. Then follow the printed instruction from
above tsh proxy aws command to add the local certificate to the Keystore.
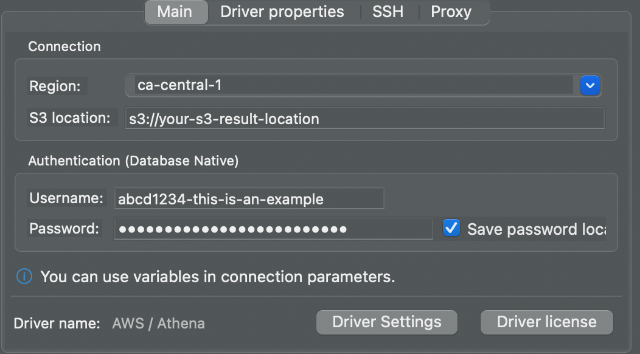
Start DBeaver and add an "Athena" connection. Enter the username (AWS access
key) and password (AWS secret key) from the tsh proxy aws output:
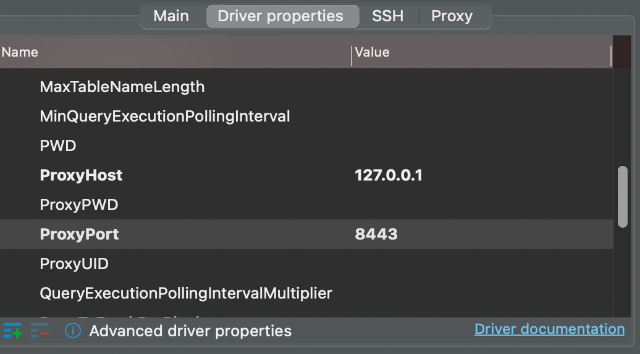
Then fill in the ProxyHost and ProxyPort settings in "Driver properties":
Click "Finish". Now you can connect to your Athena database.
By default, tsh proxy aws generates random AWS credentials for local
communication for best security and uses several placeholders in the generated
instructions. The following environment variables can be set to overwrite
those values:
TELEPORT_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: sets the local AWS access key.TELEPORT_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: sets the local AWS secret key.TELEPORT_AWS_REGION: sets the AWS region.TELEPORT_AWS_KEYSTORE: sets the Java Keystore path.TELEPORT_AWS_WORKGROUP: sets the Athena workgroup name.
tsh proxy aws generates a local certificate authority (CA) for local
communication. The local CA may expire after a new tsh login session and a
new CA will be generated. Make sure your Java Keystore is up-to-date by
deleting the alias from your Keystore and adding it again.
To log out of the aws application and remove credentials:
tsh apps logout aws
Next steps
- More information on AWS Management and API with Teleport Application Access.
- Learn more about AWS service endpoints.