Database Access with Redis Cluster
If you want to configure Redis Standalone, please read Database Access with Redis.
Teleport can provide secure access to Redis cluster via the Teleport Database Service. This allows for fine-grained access control through Teleport's RBAC.
In this guide, you will:
- Configure an Redis cluster database with mutual TLS authentication.
- Join the Redis cluster database to your Teleport cluster.
- Connect to the Redis cluster database via the Teleport Database Service.
- Self-Hosted
- Teleport Cloud
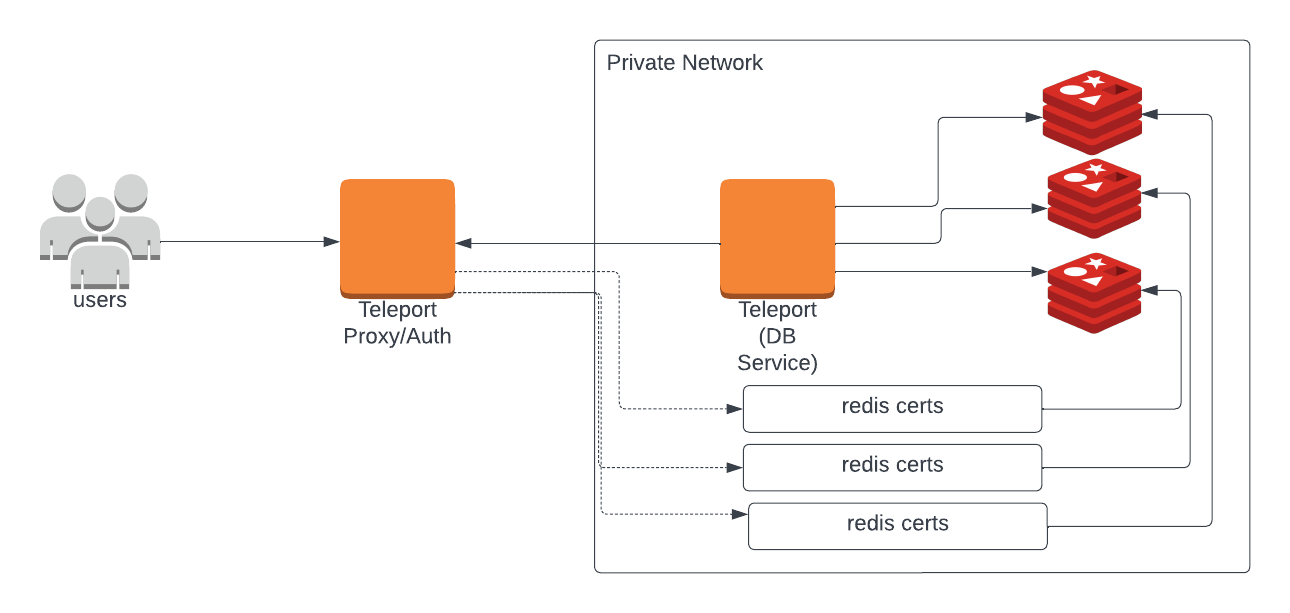
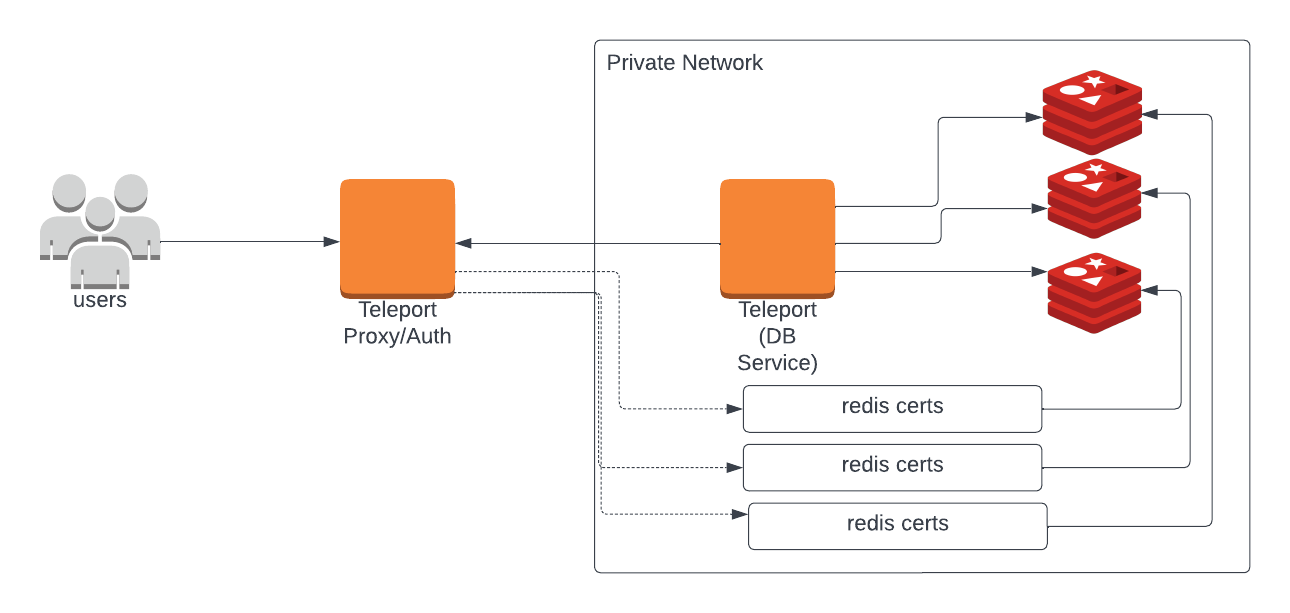
Prerequisites
-
A running Teleport cluster version 14.3.33 or above. If you want to get started with Teleport, sign up for a free trial or set up a demo environment.
-
The
tctladmin tool andtshclient tool.Visit Installation for instructions on downloading
tctlandtsh.
-
Redis version
6.0or newer.NoteRESP3 (REdis Serialization Protocol) is currently not supported.
-
redis-cliversion6.2or newer installed and added to your system'sPATHenvironment variable. -
A host where you will run the Teleport Database Service.
-
A certificate authority to issue server certificates for nodes in your Redis Cluster.
Why do I need my own CA?
Distributed databases like Redis Cluster use mTLS for node-to-node communication. Teleport requires that you have your own CA to issue certificates for node-to-node mTLS communication.
Teleport uses a split-CA architecture for database access. The Teleport
dbCA issues server certificates and thedb_clientCA issues client certificates.Databases are configured to trust the Teleport
db_clientCA for client authentication, but not thedbCA. Additionally, Teleport only issues ephemeraldb_clientCA certificates.When a Redis Cluster node connects to another Redis Cluster node, it must present a certificate that the other node trusts for client authentication. Since Teleport does not issue long-lived
db_clientcertificates, the node needs to have a long-lived certificate issued by another CA that its peer node trusts.The split
dbanddb_clientCA architecture was introduced as a security fix in Teleport versions: 13.4.17, 14.3.7, and 15.See Database CA Migrations for more information.
-
To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials.tctlis supported on macOS and Linux machines.For example:
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com [email protected]
$ tctl status
# Cluster teleport.example.com
# Version 14.3.33
# CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678If you can connect to the cluster and run the
tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions.
Step 1/6. Set up the Teleport Database Service
The Database Service requires a valid join token to join your Teleport cluster.
Run the following tctl command and save the token output in /tmp/token
on the server that will run the Database Service:
$ tctl tokens add --type=db --format=text
abcd123-insecure-do-not-use-this
Install and configure Teleport where you will run the Teleport Database Service:
- Linux Server
- Kubernetes Cluster
Select an edition, then follow the instructions for that edition to install Teleport.
- Teleport Community Edition
- Teleport Enterprise
- Teleport Enterprise Cloud
The following command updates the repository for the package manager on the local operating system and installs the provided Teleport version:
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/install-v14.3.33.sh | bash -s 14.3.33
- Debian 9+/Ubuntu 16.04+ (apt)
- Amazon Linux 2/RHEL 7 (yum)
- Amazon Linux 2/RHEL 7 (zypper)
- Amazon Linux 2023/RHEL 8+ (dnf)
- SLES 12 SP5+ and 15 SP5+ (zypper)
- Tarball
# Download Teleport's PGP public key
$ sudo curl https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/gpg \
-o /usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport APT repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc] \
https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/${ID?} ${VERSION_CODENAME?} stable/v14" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/teleport.list > /dev/null
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install teleport-ent
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo apt-get install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
# First, get the major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils
$ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/v14/teleport.repo")"
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent
#
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport Zypper repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use zypper to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh --repo $(rpm --eval "https://zypper.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-zypper.repo")
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent
#
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
# First, get the major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use the dnf config manager plugin to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/v14/teleport.repo")"
# Install teleport
$ sudo dnf install teleport-ent
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo dnf install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport Zypper repository.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use Zypper to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh --repo $(rpm --eval "https://zypper.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/v14/teleport-zypper.repo")
# Install teleport
$ sudo zypper install teleport-ent
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo zypper install teleport-ent-fips
In the example commands below, update $SYSTEM_ARCH with the appropriate
value (amd64, arm64, or arm). All example commands using this variable
will update after one is filled out.
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz.sha256
# <checksum> <filename>
$ curl -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz
$ shasum -a 256 teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz
# Verify that the checksums match
$ tar -xvf teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz
$ cd teleport-ent
$ sudo ./install
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations of Teleport Enterprise, package URLs will be slightly different:
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz.sha256
# <checksum> <filename>
$ curl -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz
$ shasum -a 256 teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz
# Verify that the checksums match
$ tar -xvf teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz
$ cd teleport-ent
$ sudo ./install
OS repository channels
The following channels are available for APT, YUM, and Zypper repos. They may be used in place of
stable/v14 anywhere in the Teleport documentation.
| Channel name | Description |
|---|---|
stable/<major> | Receives releases for the specified major release line, i.e. v14 |
stable/cloud | Rolling channel that receives releases compatible with current Cloud version |
stable/rolling | Rolling channel that receives all published Teleport releases |
- Debian 9+/Ubuntu 16.04+ (apt)
- Amazon Linux 2/RHEL 7/CentOS 7 (yum)
- Amazon Linux 2023/RHEL 8+ (dnf)
- SLES 12 SP5+ and 15 SP5+ (zypper)
Add the Teleport repository to your repository list:
# Download Teleport's PGP public key
$ sudo curl https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/gpg \
-o /usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport APT repository for cloud.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc] \
https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/${ID?} ${VERSION_CODENAME?} stable/cloud" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/teleport.list > /dev/null
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Update the repo and install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install "teleport-ent=$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for cloud.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils
$ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-yum.repo")"
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo yum install "teleport-ent-$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for cloud.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use the dnf config manager plugin to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-yum.repo")"
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo dnf install "teleport-ent-$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport Zypper repository for cloud.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use Zypper to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh --repo $(rpm --eval "https://zypper.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-zypper.repo")
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo zypper install "teleport-ent-$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
OS repository channels
The following channels are available for APT, YUM, and Zypper repos. They may be used in place of
stable/v14 anywhere in the Teleport documentation.
| Channel name | Description |
|---|---|
stable/<major> | Receives releases for the specified major release line, i.e. v14 |
stable/cloud | Rolling channel that receives releases compatible with current Cloud version |
stable/rolling | Rolling channel that receives all published Teleport releases |
Is my Teleport instance compatible with Teleport Enterprise Cloud?
Before installing a teleport binary with a version besides v16,
read our compatibility rules to ensure that the binary is compatible with
Teleport Enterprise Cloud.
Teleport uses Semantic Versioning. Version numbers
include a major version, minor version, and patch version, separated by dots.
When running multiple teleport binaries within a cluster, the following rules
apply:
- Patch and minor versions are always compatible, for example, any 8.0.1 component will work with any 8.0.3 component and any 8.1.0 component will work with any 8.3.0 component.
- Servers support clients that are one major version behind, but do not support
clients that are on a newer major version. For example, an 8.x.x Proxy Service
instance is compatible with 7.x.x agents and 7.x.x
tsh, but we don't guarantee that a 9.x.x agent will work with an 8.x.x Proxy Service instance. This also means you must not attempt to upgrade from 6.x.x straight to 8.x.x. You must upgrade to 7.x.x first. - Proxy Service instances and agents do not support Auth Service instances that
are on an older major version, and will fail to connect to older Auth Service
instances by default. You can override version checks by passing
--skip-version-checkwhen starting agents and Proxy Service instances.
On the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service, start Teleport with the appropriate configuration.
Note that a single Teleport process can run multiple different services, for
example multiple Database Service agents as well as the SSH Service or Application
Service. The step below will overwrite an existing configuration file, so if
you're running multiple services add --output=stdout to print the config in
your terminal, and manually adjust /etc/teleport.yaml.
Generate a configuration file at /etc/teleport.yaml for the Database Service:
- Teleport Enterprise/Enterprise Cloud
- Teleport Community Edition
$ sudo teleport db configure create \
-o file \
--token=/tmp/token \
--proxy=teleport.example.com:443 \
--name=example-redis \
--protocol=redis \
--uri=rediss://redis.example.com:6379?mode=cluster \
--labels=env=dev
$ sudo teleport db configure create \
-o file \
--token=/tmp/token \
--proxy=mytenant.teleport.sh:443 \
--name=example-redis \
--protocol=redis \
--uri=rediss://redis.example.com:6379?mode=cluster \
--labels=env=dev
Configure the Teleport Database Service to start automatically when the host boots up by creating a systemd service for it. The instructions depend on how you installed the Teleport Database Service.
- Package Manager
- TAR Archive
On the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service, enable and start Teleport:
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport
$ sudo systemctl start teleport
On the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service, create a systemd service configuration for Teleport, enable the Teleport service, and start Teleport:
$ sudo teleport install systemd -o /etc/systemd/system/teleport.service
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport
$ sudo systemctl start teleport
You can check the status of the Teleport Database Service with systemctl status teleport
and view its logs with journalctl -fu teleport.
Teleport provides Helm charts for installing the Teleport Database Service in Kubernetes Clusters.
Set up the Teleport Helm repository.
Allow Helm to install charts that are hosted in the Teleport Helm repository:
$ helm repo add teleport https://charts.releases.teleport.dev
Update the cache of charts from the remote repository so you can upgrade to all available releases:
$ helm repo update
- Self-Hosted
- Cloud-Hosted
Install the Teleport Kube Agent into your Kubernetes Cluster with the Teleport Database Service configuration.
$ JOIN_TOKEN=$(cat /tmp/token)
$ helm install teleport-kube-agent teleport/teleport-kube-agent \
--create-namespace \
--namespace teleport-agent \
--set roles=db \
--set proxyAddr=teleport.example.com:443 \
--set authToken=${JOIN_TOKEN?} \
--set "databases[0].name=example-redis" \
--set "databases[0].uri=rediss://redis.example.com:6379?mode=cluster" \
--set "databases[0].protocol=redis" \
--set "databases[0].static_labels.env=dev" \
--version 14.3.33
Install the Teleport Kube Agent into your Kubernetes Cluster with the Teleport Database Service configuration.
$ JOIN_TOKEN=$(cat /tmp/token)
$ helm install teleport-kube-agent teleport/teleport-kube-agent \
--create-namespace \
--namespace teleport-agent \
--set roles=db \
--set proxyAddr=mytenant.teleport.sh:443 \
--set authToken=${JOIN_TOKEN?} \
--set "databases[0].name=example-redis" \
--set "databases[0].uri=rediss://redis.example.com:6379?mode=cluster" \
--set "databases[0].protocol=redis" \
--set "databases[0].static_labels.env=dev" \
--version 16.4.3
Make sure that the Teleport agent pod is running. You should see one
teleport-kube-agent pod with a single ready container:
$ kubectl -n teleport-agent get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
teleport-kube-agent-0 1/1 Running 0 32s
A single Teleport process can run multiple services, for example multiple Database Service instances as well as other services such the SSH Service or Application Service.
Step 2/6. Create a Teleport user
To modify an existing user to provide access to the Database Service, see Database Access Access Controls
- Teleport Community Edition
- Teleport Enterprise/Enterprise Cloud
Create a local Teleport user with the built-in access role:
$ tctl users add \
--roles=access \
--db-users="*" \
--db-names="*" \
alice
Create a local Teleport user with the built-in access and requester roles:
$ tctl users add \
--roles=access,requester \
--db-users="*" \
--db-names="*" \
alice
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
--roles | List of roles to assign to the user. The builtin access role allows them to connect to any database server registered with Teleport. |
--db-users | List of database usernames the user will be allowed to use when connecting to the databases. A wildcard allows any user. |
--db-names | List of logical databases (aka schemas) the user will be allowed to connect to within a database server. A wildcard allows any database. |
Database names are only enforced for PostgreSQL and MongoDB databases.
For more detailed information about database access controls and how to restrict access see RBAC documentation.
Step 3/6. Create Redis users
Each Redis user must be protected by a strong password. We recommend using OpenSSL to generate passwords:
openssl rand -hex 32
If you have access to Redis you can also generate a password by using the below command from the Redis console:
ACL GENPASS
Create a users.acl file, which defines users for your Redis deployment, passwords required to log in as a given user,
and sets of ACL rules. Redis allows you to provide passwords in plaintext or an SHA256 hash.
We strongly recommend using an SHA256 hash instead of plaintext passwords.
You can use the command below to generate an SHA256 hash from a password.
echo -n STRONG_GENERATED_PASSWORD | sha256sum
user alice on #57639ed88a85996453555f22f5aa4147b4c9614056585d931e5d976f610651e9 allcommands allkeys
user default off
For more ACL examples refer to the Redis documentation.
It's very important to either disable or protect with a password the default user. Otherwise, everyone with access
to the database can log in as the default user, which by default has administrator privileges.
Step 4/6. Set up mutual TLS
Export your Teleport cluster's db_client CA cert and concatenate it with your Redis
Cluster's CA cert (in PEM format):
$ tctl auth export --type=db-client > db-client-ca.crt
$ cat /path/to/your/ca.crt db-client-ca.crt > pem-bundle.cas
Using your Redis Cluster's CA, issue server.crt for each of your Redis Cluster
nodes and enable mutual TLS in your redis.conf configuration file, then
restart each node:
tls-port 7001
port 0
cluster-enabled yes
tls-replication yes
tls-cluster yes
aclfile /path/to/users.acl
masterauth GENERATED_STRONG_PASSWORD
masteruser replica-user
tls-cert-file /usr/local/etc/redis/certs/server.crt
tls-key-file /usr/local/etc/redis/certs/server.key
tls-ca-cert-file /usr/local/etc/redis/certs/pem-bundle.cas
tls-protocols "TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3"
Once mutual TLS has been enabled, you will no longer be able to connect to
the cluster without providing a valid client certificate. You can use the
tls-auth-clients optional setting to allow connections
from clients that do not present a certificate.
See TLS Support in the Redis documentation for more details.
Modify the Teleport Database Service to trust your Redis Cluster CA:
databases:
- name: "example-redis"
protocol: "redis"
uri: "rediss://redis.example.com:6379?mode=cluster"
static_labels:
"env": "example"
tls:
ca_cert_file: "undefined"
Now the Teleport Database Service will trust certificates presented by your Redis Cluster.
Step 5/6. Create a cluster
To create the cluster after mutual TLS is enabled, you will need to use a
certificate that the Redis nodes trust for client authentication.
You can use a certificate that you already issued for one of the nodes, i.e.
server.crt or you can issue a new client certificate using your Redis Cluster
CA.
Use the following command to create the cluster. Please note redis-cli --cluster create accepts only IP addresses.
$ export REDISCLI_AUTH=STRONG_GENERATED_PASSWORD
$ export CERTS_DIR=/path/to/certs/
$ export IP1=10.0.0.1 # update with the real node 1 IP
$ export IP2=10.0.0.2 # update with the real node 2 IP
$ export IP3=10.0.0.3 # update with the real node 3 IP
$ export IP4=10.0.0.4 # update with the real node 4 IP
$ export IP5=10.0.0.5 # update with the real node 5 IP
$ export IP6=10.0.0.6 # update with the real node 6 IP
$ redis-cli --user alice --cluster-replicas 1 --tls --cluster-yes \
--cluster create ${IP1}:7001 ${IP2}:7002 ${IP3}:7003 ${IP4}:7004 ${IP5}:7005 ${IP6}:7006 \
--cacert ${CERTS_DIR}/ca.crt --key ${CERTS_DIR}/server.key --cert ${CERTS_DIR}/server.crt
Step 6/6. Connect
To enable Redis cluster mode in Teleport, add the mode=cluster parameter to the connection URI in
your Teleport Database Service config file.
databases:
- name: "redis-cluster"
uri: "rediss://redis.example.com:6379?mode=cluster"
Log into your Teleport cluster and see available databases:
- Self-Hosted
- Cloud-Hosted
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=alice
$ tsh db ls
# Name Description Labels
# ------------- --------------- --------
# example-redis Example Redis env=dev
$ tsh login --proxy=mytenant.teleport.sh --user=alice
$ tsh db ls
# Name Description Labels
# ------------- --------------- --------
# example-redis Example Redis env=dev
To connect to a particular database instance:
$ tsh db connect example-redis
You can optionally specify the database user to use by default when connecting to the database instance:
$ tsh db connect --db-user=alice example-redis
If flag --db-user is not provided, Teleport logs in as the default user.
Now you can log in as the previously created user using the below command:
AUTH alice STRONG_GENERATED_PASSWORD
To log out of the database and remove credentials:
# Remove credentials for a particular database instance.
$ tsh db logout example-redis
# Remove credentials for all database instances.
$ tsh db logout
Supported Redis Cluster commands
Redis in cluster mode does not support the following commands. If one of the listed commands above is called Teleport
returns the ERR Teleport: command not supported
Unsupported commands
ACLASKINGCLIENTCLUSTERCONFIGDEBUGEXECHELLOINFOLATENCYMEMORYMIGRATEMODULEMONITORMULTIPFDEBUGPFSELFTESTPSUBSCRIBEPSYNCPUNSUBSCRIBEPUNSUBSCRIBEREADONLYREADWRITEREPLCONFREPLICAOFROLESCANSCRIPT DEBUGSCRIPT KILLSHUTDOWNSLAVEOFSLOWLOGSSUBSCRIBESUNSUBSCRIBESYNCTIMEWAITWATCH
Teleport conducts additional processing on the following commands before communicating with Redis Cluster:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
DBSIZE | Sends the query to all nodes and returns the number of keys in the whole cluster. |
KEYS | Sends the query to all nodes and returns a list of all keys in the whole cluster. |
MGET | Translates the commands to multiple GETs and sends them to multiple nodes. Result is merged in Teleport and returned back to the client. If Teleport fails to fetch at least one key an error is returned. |
FLUSHDB | Sends the query to all nodes. |
FLUSHALL | Works the same as FLUSHDB. |
SCRIPT EXISTS | Sends the query to all nodes. 1 is returned only if script exists on all nodes. |
SCRIPT LOAD | Sends the script to all nodes. |
SCRIPT FLUSH | Sends the query to all nodes. ASYNC parameter is ignored. |
Next steps
- Learn how to restrict access to certain users and databases.
- Learn more about dynamic database registration.
- View the High Availability (HA) guide.
- See the YAML configuration reference for updating dynamic resource matchers or static database definitions.
- Take a look at the full CLI reference.