Table Of Contents
Home - Teleport Blog - Teleport 4.4: Concurrent Session Control & Session Streaming - Oct 20, 2020
Teleport 4.4: Concurrent Session Control & Session Streaming

What is SSH Session Control?
A SSH session can be interactive or non-interactive. The session starts when a computer or human connects to a node using SSH. SSH sessions can be established using public/private key cryptography or can use short lived SSH Certificates, similar to how Teleport works. Organizations often want to know who is accessing the systems and provide a greater level of control over who and when people are accessing them, which is where Teleport 4.4 comes into play.
Concurrent Current Session Control
This addition to Teleport helps customers obtain AC-10 control. For our customers who are on the FedRAMP journey or who are trying to limit sessions, we’ve added some new knobs to control how Teleport Server Sessions work.
We now provide two new optional configuration values max_connections and max_sessions.
max_connections
This value is the total number of concurrent sessions to nodes within a Teleport cluster. This value is applied at a per user level. If you set max_connections to 1, a tsh user would only be able to tsh ssh into a node at one time. If you use Tmux this would count as one session, as the multiplexer is shared over the one connection.
max_sessions ( per connection )
This value limits the total number of session channels that can be established across a single SSH connection (typically used for interactive terminals or remote exec operations). This is for cases in which nodes have Teleport set up, but the developer is using OpenSSH to connect to them. It is essentially equivalent to the MaxSessions configuration value accepted by sshd.
Example Teleport Role
kind: role
metadata:
name: limited-ssh-session-user
# ...
spec:
options:
# Optional: Required to be set for AC-10 Compliance
max_connections: 2
# Optional: To match OpenSSH behavior set to 10
max_sessions: 10
# ...
version: v3
In the above example, a user can connect to two nodes using TSH or the UI. If the developer is using OpenSSH on the client, they’ll be able to open 10 session channels per SSH Connection.
Cluster Configuration
A new session_control_timeout configuration value has been added to the auth_service configuration block of the teleport config file: Because the value maps cluster wide, if the node can. You won’t likely need to change this.
auth_service:
session_control_timeout: 2m # default
# ...
Audit Events
Attempts to exceed the max_connections and max_sessions restraints result in two new events in the Teleport Audit Log.
{
"code": "T1006W",
"event": "sessctl.limit",
"max": 2,
"proto": "ssh",
"server_id": "dc43a481-3063-4476-a9c7-505d1fffc077",
"sessctl_kind": "connection",
"time": "2020-08-25T20:55:28.548Z",
"uid": "adfad7cd-e884-47dd-8663-4d83de30f7cc",
"user": "alice"
}
Beta Session Streaming
This release has completed a large refactoring for Teleport Sessions. This version provides developers the ability to stream sessions directly to a storage provider. This feature can help with performance, as long sessions don’t take up a lot of space on disk. This provides an added security benefit of sessions never touching the disk of the host.
How does it work?
The grey line shows a session being connected to a node. Once the session starts, the events will be streamed during the session.
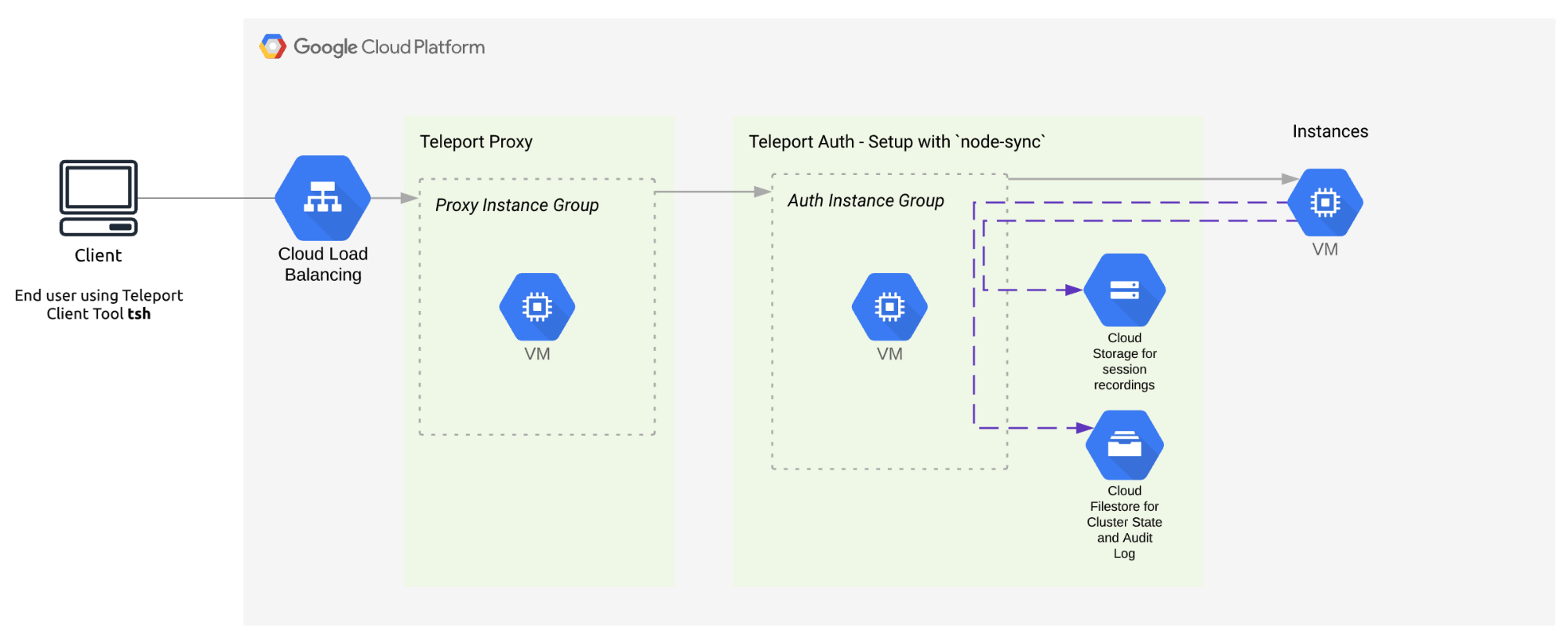

Supported Backends
This feature has been designed and tested with S3, Google Cloud Storage (GCS), and S3-compatible backends such as IBM Cloud Object Storage. We also support local file storage and multipart upload (by storing each uploaded part in a separate file).
This feature is supported and tested for Teleport Kubernetes Access customers.
Setup in teleport.yaml
This feature is configured to be cluster wide. Most customers should start with node-sync.
# This section configures the 'auth service':
auth_service:
# Optional setting for configuring session recording. Possible values are:
# "node" : sessions will be recorded on the node level (the default)
# "proxy" : recording on the proxy level, see "recording proxy mode" section.
# "off" : session recording is turned off
#
# EXPERIMENTAL *-sync modes proxy and node sends logs directly to S3 or other
# storage without storing the records on disk at all. This mode will kill a
# connection if network connectivity is lost.
#
# "node-sync" : sessions recording will be streamed from node -> auth -> storage service
# "proxy-sync : sessions recording will be streamed from proxy -> auth -> storage service
#
session_recording: "node-sync"
Improvements
- Session streams structured events. #4045
- Add ability to specify leaf cluster when generating kubeconfig via
tctl auth sign#4446 - Add output options for
tsh ls#4390 - Concurrent Session Control #4138
- Add nodeID to heartbeat debug log #4291
- Optional: trigger pam_authenticate on login #3966
Teleport cybersecurity blog posts and tech news
Every other week we'll send a newsletter with the latest cybersecurity news and Teleport updates.
Fixes
- k8s: enable SPDY pings on in/outbound connections #4377
- Updated github.com/russellhaering/goxmldsig to v1.1.0 #4396
- remove symlink usage for tsh profile #4347
- Always collect metrics about top backend requests #4282
- DynamoDB respect HTTP Connect proxies #4271
- Get teleport /readyz state from heartbeats instead of cert rotation #4223
- Lookup and return hostname as part of new UI session request #4239
- tctl: fix
tctl topcolors on dark terminals #4231 - Audit log will include session.rejected events when using session control #4458
Upgrade Notes
Always follow the recommended upgrade procedure to upgrade to this version.
Tags
Teleport Newsletter
Stay up-to-date with the newest Teleport releases by subscribing to our monthly updates.

Subscribe to our newsletter

