
Teleport
Export Events with Fluentd
- Version 17.x
- Version 16.x
- Version 15.x
- Version 14.x
- Older Versions
Forwarding Access Logs using FluentD
Length: 18:36
Fluentd is an open source data collector for a unified logging layer. In this guide, we will:
- Set up Teleport's Event Handler plugin.
- Forward events with Fluentd.
This guide also serves as an explanation for the Teleport Event Handler plugin, using Fluentd as the target service. We'll create a local Docker container as a destination for the Event Handler:
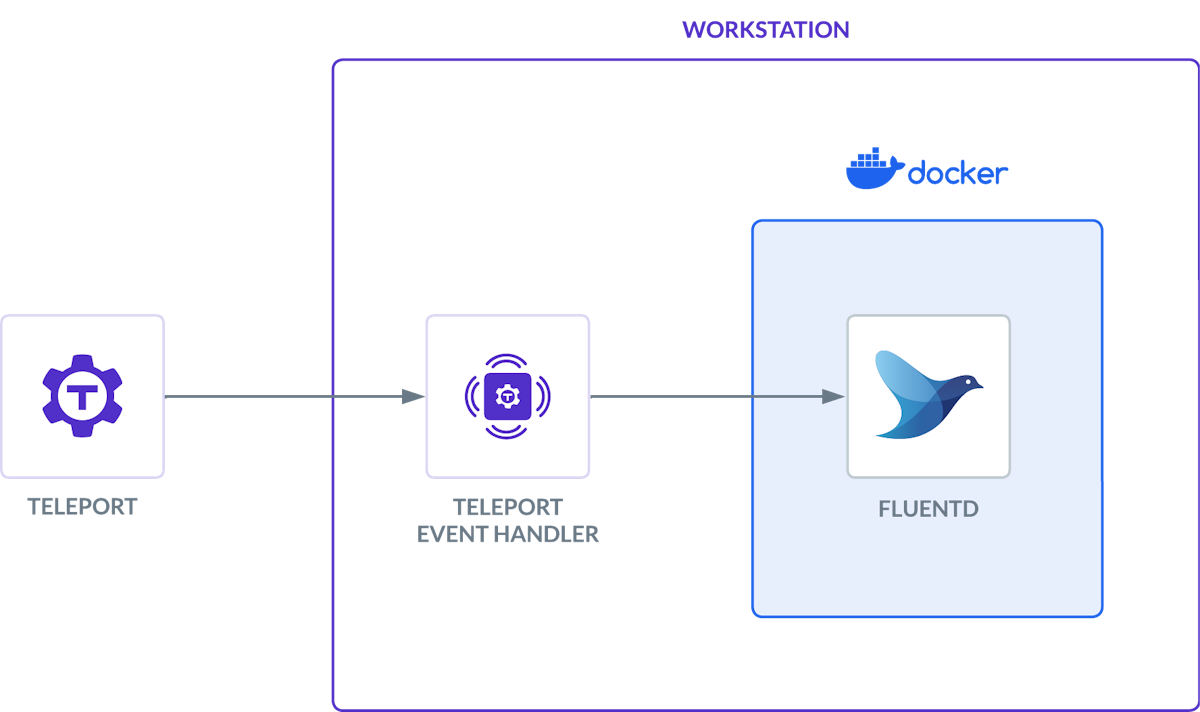
You can follow the instructions below for a local proof-of-concept demo, or use any of the additional installation instructions to configure the Teleport Event Handler to integrate with your infrastructure.
Prerequisites
-
A running Teleport cluster version 16.1.0 or above. If you want to get started with Teleport, sign up for a free trial or set up a demo environment.
-
The
tctladmin tool andtshclient tool.Visit Installation for instructions on downloading
tctlandtsh.
Recommended: Configure Machine ID to provide short-lived Teleport
credentials to the plugin. Before following this guide, follow a Machine ID
deployment guide to run the tbot binary on
your infrastructure.
-
Fluentd version v1.12.4 or greater.
-
Docker version v20.10.7.
-
To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials.tctlis supported on macOS and Linux machines.For example:
tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=[email protected]tctl statusCluster teleport.example.com
Version 16.1.0
CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678
If you can connect to the cluster and run the
tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions. -
On your workstation, create a folder called
event-handler, to hold configuration files and plugin state:mkdir -p event-handlercd event-handler
Step 1/6. Install the event handler plugin
The Teleport event handler runs alongside the Fluentd forwarder, receives events from Teleport's events API, and forwards them to Fluentd.
The Event Handler plugin is provided in amd64 and arm64 binaries for downloading.
Replace ARCH with your required version.
curl -L -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-event-handler-v16.1.0-linux-ARCH-bin.tar.gztar -zxvf teleport-event-handler-v16.1.0-linux-ARCH-bin.tar.gzsudo ./teleport-event-handler/install
The Event Handler plugin is provided in amd64 and arm64 binaries for downloading.
Replace ARCH with your required version.
curl -L -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-event-handler-v16.1.0-darwin-ARCH-bin.tar.gztar -zxvf teleport-event-handler-v16.1.0-darwin-ARCH-bin.tar.gzsudo ./teleport-event-handler/install
Ensure that you have Docker installed and running.
docker pull public.ecr.aws/gravitational/teleport-plugin-event-handler:16.1.0
To allow Helm to install charts that are hosted in the Teleport Helm repository, use helm repo add:
helm repo add teleport https://charts.releases.teleport.dev
To update the cache of charts from the remote repository, run helm repo update:
helm repo update
You will need Go >= 1.22 installed.
Run the following commands on your Universal Forwarder host:
git clone https://github.com/gravitational/teleport.git --depth 1 -b branch/v16cd teleport/integrations/event-handlergit checkout 16.1.0make build
The resulting executable will have the name event-handler. To follow the
rest of this guide, rename this file to teleport-event-handler and move it
to /usr/local/bin.
Step 2/6. Generate a plugin configuration
Run the configure command to generate a sample configuration. Replace
mytenant.teleport.sh with the DNS name of your Teleport Enterprise Cloud
tenant:
teleport-event-handler configure . mytenant.teleport.sh:443
Run the configure command to generate a sample configuration. Replace
teleport.example.com:443 with the DNS name and HTTPS port of Teleport's Proxy
Service:
teleport-event-handler configure . teleport.example.com:443
Run the configure command to generate a sample configuration. Assign
TELEPORT_CLUSTER_ADDRESS to the DNS name and port of your Teleport Auth
Service or Proxy Service:
TELEPORT_CLUSTER_ADDRESS=mytenant.teleport.sh:443docker run -v `pwd`:/opt/teleport-plugin -w /opt/teleport-plugin public.ecr.aws/gravitational/teleport-plugin-event-handler:16.1.0 configure . ${TELEPORT_CLUSTER_ADDRESS?}
In order to export audit events, you'll need to have the root certificate and the client credentials available as a secret. Use the following command to create that secret in Kubernetes:
kubectl create secret generic teleport-event-handler-client-tls --from-file=ca.crt=ca.crt,client.crt=client.crt,client.key=client.key
This will pack the content of ca.crt, client.crt, and client.key into the
secret so the Helm chart can mount them to their appropriate path.
You'll see the following output:
Teleport event handler 16.1.0
[1] mTLS Fluentd certificates generated and saved to ca.crt, ca.key, server.crt, server.key, client.crt, client.key
[2] Generated sample teleport-event-handler role and user file teleport-event-handler-role.yaml
[3] Generated sample fluentd configuration file fluent.conf
[4] Generated plugin configuration file teleport-event-handler.toml
The plugin generates several setup files:
ls -l-rw------- 1 bob bob 1038 Jul 1 11:14 ca.crt
-rw------- 1 bob bob 1679 Jul 1 11:14 ca.key
-rw------- 1 bob bob 1042 Jul 1 11:14 client.crt
-rw------- 1 bob bob 1679 Jul 1 11:14 client.key
-rw------- 1 bob bob 541 Jul 1 11:14 fluent.conf
-rw------- 1 bob bob 1078 Jul 1 11:14 server.crt
-rw------- 1 bob bob 1766 Jul 1 11:14 server.key
-rw------- 1 bob bob 260 Jul 1 11:14 teleport-event-handler-role.yaml
-rw------- 1 bob bob 343 Jul 1 11:14 teleport-event-handler.toml
| File(s) | Purpose |
|---|---|
ca.crt and ca.key | Self-signed CA certificate and private key for Fluentd |
server.crt and server.key | Fluentd server certificate and key |
client.crt and client.key | Fluentd client certificate and key, all signed by the generated CA |
teleport-event-handler-role.yaml | user and role resource definitions for Teleport's event handler |
fluent.conf | Fluentd plugin configuration |
This guide assumes that you are running the Event Handler on the same host or
Kubernetes pod as your log forwarder. If you are not, you will need to instruct
the Event Handler to generate mTLS certificates for subjects besides
localhost. To do this, use the --cn and --dns-names flags of the
teleport-event-handler configure command.
For example, if your log forwarder is addressable at forwarder.example.com and the
Event Handler at handler.example.com, you would run the following configure
command:
teleport-event-handler configure --cn=handler.example.com --dns-names=forwarder.example.com
The command generates client and server certificates with the subjects set to
the value of --cn.
The --dns-names flag accepts a comma-separated list of DNS names. It will
append subject alternative names (SANs) to the server certificate (the one you
will provide to your log forwarder) for each DNS name in the list. The Event
Handler looks up each DNS name before appending it as an SAN and exits with an
error if the lookup fails.
If you have an existing Fluentd setup with TLS, issue a client certificate and key from the same certificate authority for the Teleport Event Handler to use.
Step 3/6. Create a user and role for reading audit events
The teleport-event-handler configure command generated a file called
teleport-event-handler-role.yaml. This file defines a teleport-event-handler
role and a user with read-only access to the event API:
kind: role
metadata:
name: teleport-event-handler
spec:
allow:
rules:
- resources: ['event', 'session']
verbs: ['list','read']
version: v5
---
kind: user
metadata:
name: teleport-event-handler
spec:
roles: ['teleport-event-handler']
version: v2
Move this file to your workstation (or recreate it by pasting the snippet above)
and use tctl on your workstation to create the role and the user:
tctl create -f teleport-event-handler-role.yamluser "teleport-event-handler" has been created
role 'teleport-event-handler' has been created
Step 4/6. Create teleport-event-handler credentials
Enable issuing of credentials for the event handler role
With the role created, you now need to allow the Machine ID bot to produce credentials for this role.
This can be done with tctl, replacing my-bot with the name of your bot:
tctl bots update my-bot --add-roles teleport-event-handler
In order for the Event Handler plugin to forward events from your Teleport
cluster, it needs signed credentials from the cluster's certificate authority.
The teleport-event-handler user cannot request this itself, and requires
another user to impersonate this account in order to request credentials.
Create a role that enables your user to impersonate the teleport-event-handler
user. First, paste the following YAML document into a file called
teleport-event-handler-impersonator.yaml:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: teleport-event-handler-impersonator
spec:
options:
# max_session_ttl defines the TTL (time to live) of SSH certificates
# issued to the users with this role.
max_session_ttl: 10h
# This section declares a list of resource/verb combinations that are
# allowed for the users of this role. By default nothing is allowed.
allow:
impersonate:
users: ["teleport-event-handler"]
roles: ["teleport-event-handler"]
Next, create the role:
tctl create teleport-event-handler-impersonator.yaml
Add this role to the user that generates signed credentials for the Event Handler:
Assign the teleport-event-handler-impersonator role to your Teleport user by running the appropriate
commands for your authentication provider:
-
Retrieve your local user's roles as a comma-separated list:
ROLES=$(tsh status -f json | jq -r '.active.roles | join(",")') -
Edit your local user to add the new role:
tctl users update $(tsh status -f json | jq -r '.active.username') \ --set-roles "${ROLES?},teleport-event-handler-impersonator" -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
githubauthentication connector:tctl get github/github --with-secrets > github.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto thegithub.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the github.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
github.yaml, addingteleport-event-handler-impersonatorto theteams_to_rolessection.The team you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the team must include your user account and should be the smallest team possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
teams_to_roles: - organization: octocats team: admins roles: - access + - teleport-event-handler-impersonator -
Apply your changes:
tctl create -f github.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
samlconfiguration resource:tctl get --with-secrets saml/mysaml > saml.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto thesaml.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the saml.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
saml.yaml, addingteleport-event-handler-impersonatorto theattributes_to_rolessection.The attribute you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the group must include your user account and should be the smallest group possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
attributes_to_roles: - name: "groups" value: "my-group" roles: - access + - teleport-event-handler-impersonator -
Apply your changes:
tctl create -f saml.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
oidcconfiguration resource:tctl get oidc/myoidc --with-secrets > oidc.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto theoidc.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the oidc.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
oidc.yaml, addingteleport-event-handler-impersonatorto theclaims_to_rolessection.The claim you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the group must include your user account and should be the smallest group possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
claims_to_roles: - name: "groups" value: "my-group" roles: - access + - teleport-event-handler-impersonator -
Apply your changes:
tctl create -f oidc.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
Export an identity file for the Fluentd plugin user
Give the plugin access to a Teleport identity file. We recommend using Machine
ID for this in order to produce short-lived identity files that are less
dangerous if exfiltrated, though in demo deployments, you can generate
longer-lived identity files with tctl:
Configure tbot with an output that will produce the credentials needed by
the plugin. As the plugin will be accessing the Teleport API, the correct
output type to use is identity.
For this guide, the directory destination will be used. This will write these
credentials to a specified directory on disk. Ensure that this directory can
be written to by the Linux user that tbot runs as, and that it can be read by
the Linux user that the plugin will run as.
Modify your tbot configuration to add an identity output.
If running tbot on a Linux server, use the directory output to write
identity files to the /opt/machine-id directory:
outputs:
- type: identity
destination:
type: directory
# For this guide, /opt/machine-id is used as the destination directory.
# You may wish to customize this. Multiple outputs cannot share the same
# destination.
path: /opt/machine-id
If running tbot on Kubernetes, write the identity file to Kubernetes secret
instead:
outputs:
- type: identity
destination:
type: kubernetes_secret
name: teleport-event-handler-identity
If operating tbot as a background service, restart it. If running tbot in
one-shot mode, execute it now.
You should now see an identity file under /opt/machine-id or a Kubernetes
secret named teleport-event-handler-identity. This contains the private key and signed
certificates needed by the plugin to authenticate with the Teleport Auth
Service.
Like all Teleport users, teleport-event-handler needs signed credentials in order to
connect to your Teleport cluster. You will use the tctl auth sign command to
request these credentials.
The following tctl auth sign command impersonates the teleport-event-handler user,
generates signed credentials, and writes an identity file to the local
directory:
tctl auth sign --user=teleport-event-handler --out=identity
The plugin connects to the Teleport Auth Service's gRPC endpoint over TLS.
The identity file, identity, includes both TLS and SSH credentials. The
plugin uses the SSH credentials to connect to the Proxy Service, which
establishes a reverse tunnel connection to the Auth Service. The plugin
uses this reverse tunnel, along with your TLS credentials, to connect to the
Auth Service's gRPC endpoint.
By default, tctl auth sign produces certificates with a relatively short
lifetime. For production deployments, we suggest using Machine
ID to programmatically issue and renew
certificates for your plugin. See our Machine ID getting started
guide to learn more.
Note that you cannot issue certificates that are valid longer than your existing credentials.
For example, to issue certificates with a 1000-hour TTL, you must be logged in with a session that is
valid for at least 1000 hours. This means your user must have a role allowing
a max_session_ttl of at least 1000 hours (60000 minutes), and you must specify a --ttl
when logging in:
tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --ttl=60060
If you are running the plugin on a Linux server, create a data directory to hold certificate files for the plugin:
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/teleport/api-credentialssudo mv identity /var/lib/teleport/plugins/api-credentials
If you are running the plugin on Kubernetes, Create a Kubernetes secret that contains the Teleport identity file:
kubectl -n teleport create secret generic --from-file=identity teleport-event-handler-identity
Once the Teleport credentials expire, you will need to renew them by running the
tctl auth sign command again.
Step 5/6. Start the Fluentd forwarder
The Fluentd plugin will send events to your Fluentd instance using keys generated on the previous step.
The fluent.conf file generated earlier configures your Fluentd instance to
accept events using TLS and print them:
<source>
@type http
port 8888
<transport tls>
client_cert_auth true
# We are going to run fluentd in Docker. /keys will be mounted from the host file system.
ca_path /keys/ca.crt
cert_path /keys/server.crt
private_key_path /keys/server.key
private_key_passphrase ********** # Passphrase generated along with the keys
</transport>
<parse>
@type json
json_parser oj
# This time format is used by the plugin. This field is required.
time_type string
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S
</parse>
# If the number of events is high, fluentd will start failing the ingestion
# with the following error message: buffer space has too many data errors.
# The following configuration prevents data loss in case of a restart and
# overcomes the limitations of the default fluentd buffer configuration.
# This configuration is optional.
# See https://docs.fluentd.org/configuration/buffer-section for more details.
<buffer>
@type file
flush_thread_count 8
flush_interval 1s
chunk_limit_size 10M
queue_limit_length 16
retry_max_interval 30
retry_forever true
</buffer>
</source>
# Events sent to test.log will be dumped to STDOUT.
<match test.log>
@type stdout
</match>
To try out this Fluentd configuration, start your fluentd instance:
docker run -u $(id -u ${USER}):$(id -g ${USER}) -p 8888:8888 -v $(pwd):/keys -v $(pwd)/fluent.conf:/fluentd/etc/fluent.conf fluent/fluentd:edge
This will consume your current terminal, so open a new one to continue following along.
Step 6/6. Run the Event Handler plugin
Configure the Event Handler
In this section, you will configure the Teleport Event Handler for your environment.
Earlier, we generated a file called teleport-event-handler.toml to configure
the Fluentd event handler. This file includes setting similar to the following:
storage = "./storage"
timeout = "10s"
batch = 20
namespace = "default"
# The window size configures the duration of the time window for the event handler
# to request events from Teleport. By default, this is set to 24 hours.
# Reduce the window size if the events backend cannot manage the event volume
# for the default window size.
# The window size should be specified as a duration string, parsed by Go's time.ParseDuration.
window-size = "24h"
[forward.fluentd]
ca = "/home/bob/event-handler/ca.crt"
cert = "/home/bob/event-handler/client.crt"
key = "/home/bob/event-handler/client.key"
url = "https://fluentd.example.com:8888/test.log"
session-url = "https://fluentd.example.com:8888/session"
[teleport]
addr = "example.teleport.com:443"
identity = "identity"
Modify the configuration to replace fluentd.example.com with the domain name
of your Fluentd deployment.
Use the following template to create teleport-plugin-event-handler-values.yaml:
eventHandler:
storagePath: "./storage"
timeout: "10s"
batch: 20
namespace: "default"
# The window size configures the duration of the time window for the event handler
# to request events from Teleport. By default, this is set to 24 hours.
# Reduce the window size if the events backend cannot manage the event volume
# for the default window size.
# The window size should be specified as a duration string, parsed by Go's time.ParseDuration.
windowSize: "24h"
teleport:
address: "example.teleport.com:443"
identitySecretName: teleport-event-handler-identity
identitySecretPath: identity
fluentd:
url: "https://fluentd.fluentd.svc.cluster.local/events.log"
sessionUrl: "https://fluentd.fluentd.svc.cluster.local/session.log"
certificate:
secretName: "teleport-event-handler-client-tls"
caPath: "ca.crt"
certPath: "client.crt"
keyPath: "client.key"
persistentVolumeClaim:
enabled: true
Next, modify the configuration file as follows:
addr: Include the hostname and HTTPS port of your Teleport Proxy Service
or Teleport Enterprise Cloud tenant (e.g., teleport.example.com:443 or
mytenant.teleport.sh:443).
identity: Fill this in with the path to the identity file you exported
earlier.
client_key, client_crt, root_cas: Comment these out, since we
are not using them in this configuration.
address: Include the hostname and HTTPS port of your Teleport Proxy Service
or Teleport Enterprise Cloud tenant (e.g., teleport.example.com:443 or
mytenant.teleport.sh:443).
identitySecretName: Fill in the identitySecretName field with the name
of the Kubernetes secret you created earlier.
identitySecretPath: Fill in the identitySecretPath field with the path
of the identity file within the Kubernetes secret. If you have followed the
instructions above, this will be identity.
If you are providing credentials to the Event Handler using a tbot binary that
runs on a Linux server, make sure the value of identity in the Event Handler
configuration is the same as the path of the identity file you configured tbot
to generate, /opt/machine-id/identity.
Start the Teleport Event Handler
Start the Teleport Teleport Event Handler by following the instructions below.
Copy the teleport-event-handler.toml file to /etc on your Linux server.
Update the settings within the toml file to match your environment. Make sure to
use absolute paths on settings such as identity and storage. Files
and directories in use should only be accessible to the system user executing
the teleport-event-handler service such as /var/lib/teleport-event-handler.
Next, create a systemd service definition at the path
/usr/lib/systemd/system/teleport-event-handler.service with the following
content:
[Unit]
Description=Teleport Event Handler
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/teleport-event-handler start --config=/etc/teleport-event-handler.toml --teleport-refresh-enabled=true
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
PIDFile=/run/teleport-event-handler.pid
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
If you are not using Machine ID to provide short-lived credentials to the Event
Handler, you can remove the --teleport-refresh-enabled true flag.
Enable and start the plugin:
sudo systemctl enable teleport-event-handlersudo systemctl start teleport-event-handler
You can configure when you would like the Teleport Event Handler to begin
exporting events when you run the start command. This example will start
exporting from May 5th, 2021:
teleport-event-handler start --config /etc/teleport-event-handler.toml --start-time "2021-05-05T00:00:00Z"
You can only determine the start time once, when first running the Teleport
Event Handler. If you want to change the time frame later, remove the plugin
state directory that you specified in the storage field of the handler's
configuration file.
Once the Teleport Event Handler starts, you will see notifications about scanned and forwarded events:
sudo journalctl -u teleport-event-handlerDEBU Event sent id:f19cf375-4da6-4338-bfdc-e38334c60fd1 index:0 ts:2022-09-2118:51:04.849 +0000 UTC type:cert.create event-handler/app.go:140...
Run the following command on your workstation:
helm install teleport-plugin-event-handler teleport/teleport-plugin-event-handler \ --values teleport-plugin-event-handler-values.yaml \ --version 16.1.0
Troubleshooting connection issues
If the Teleport Event Handler is displaying error logs while connecting to your Teleport Cluster, ensure that:
- The certificate the Teleport Event Handler is using to connect to your
Teleport cluster is not past its expiration date. This is the value of the
--ttlflag in thetctl auth signcommand, which is 12 hours by default. - Ensure that in your Teleport Event Handler configuration file
(
teleport-event-handler.toml), you have provided the correct host and port for the Teleport Proxy Service or Auth Service.
Next Steps
Read more about impersonation here.
While this guide uses the tctl auth sign command to issue credentials for the
Teleport Event Handler, production clusters should use Machine ID for safer,
more reliable renewals. Read our guide
to getting started with Machine ID.
To see all of the options you can set in the values file for the
teleport-plugin-event-handler Helm chart, consult our reference
guide.