Teleport Blog - What Is AAA Security? - Feb 16, 2022
What Is AAA Security?
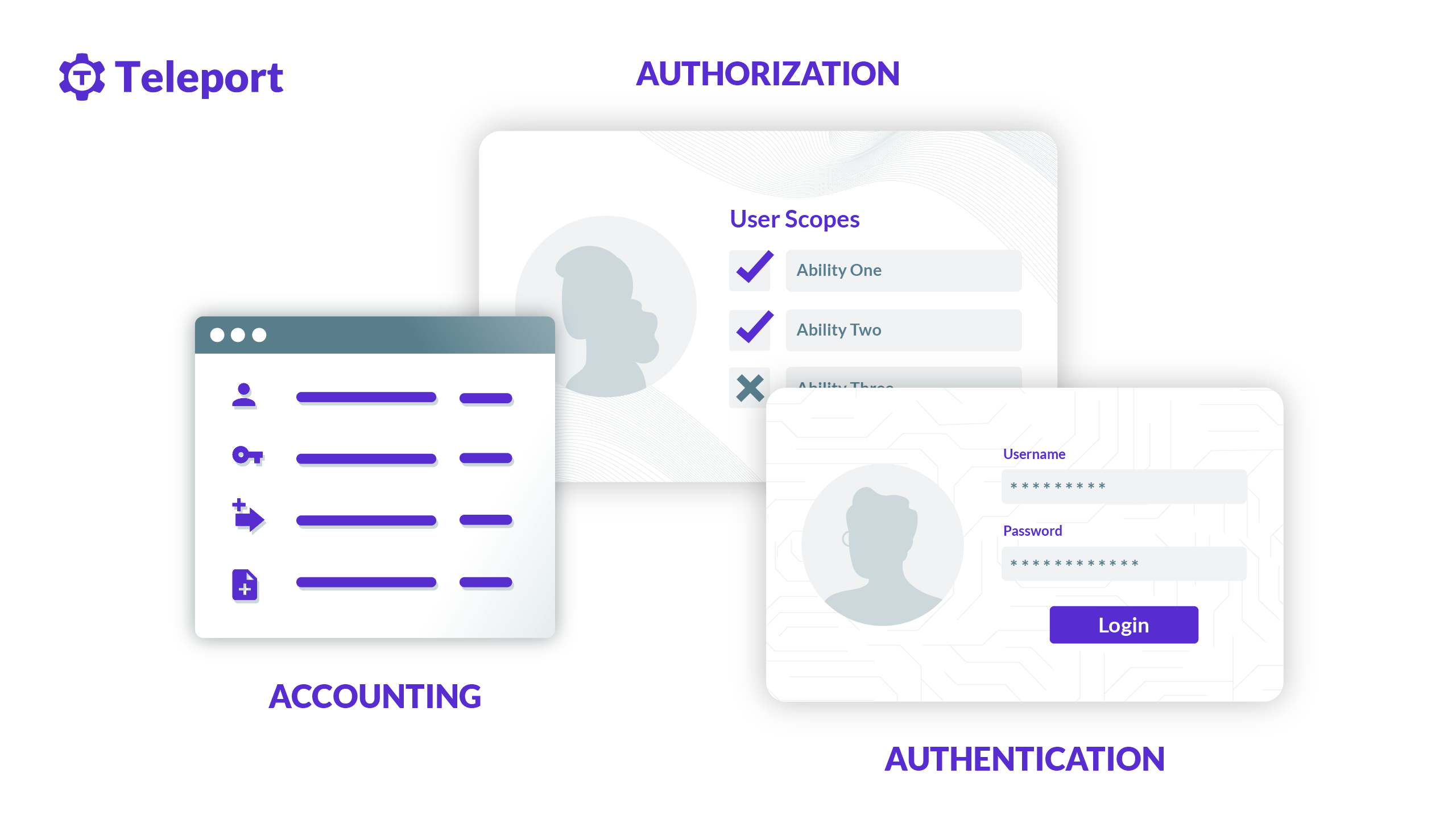
Authentication, authorization, and accounting, often called AAA or Triple-A, are sets of services and protocols that enable granular access control over computer networks. Before the popularity of mainstream HTTP-based authentication protocols such as OAuth and SAML, AAA protocols were the primary way to authenticate users or machines to network services. AAA protocols are still commonly found in corporate LAN and WAN networks, ISPs, cellular networks, and network devices such as firewalls, routers, and switches.
AAA is an important topic in network access control, and this blog post will briefly explain the primary concepts and examples of AAA protocols. If you are new to access control concepts, our blog on authentication vs. authorization is the recommended place to start.
What are AAA protocols?
AAA stands for authentication, authorization, and accounting. Authentication involves verifying the authenticity of users’ or machines’ identities; authorization involves granting permissions to read, update configuration files or execute programs; and accounting involves measuring a user’s or machine’s resource usage in an authenticated session.
AAA protocols are primarily used for network access control (LAN, WAN resources) and network device administration (firewall, routers switches). AAA protocols were designed as a centralized way to implement access control covering authentication, authorization, and accounting capabilities. Below is how AAA protocols add values to users, administrators and network service providers.
- For network service providers and vendors: Feature-rich access control methods can be out of scope for network service providers or network device manufacturers. Supporting standardized protocols defers functionality and security to well-defined and acclaimed protocols.
- For administrators: It can be challenging to design proper access control solutions in a network that comprises devices from different vendors. Implementing access controls based on standard protocols helps integrate best-of-breed products from different vendors.
- For users: It can quickly become impractical for users to have an individual account for each different network service and device. In a centralized AAA-implemented network, administrators usually implement single sign-on (SSO), allowing users to access network resources with a single identity and credential.
AAA protocols help implement secure and uniform access controls to network resources and devices at scale. RADIUS, TACACS+, and Diameter are the three most popular and widely implemented AAA protocols. These protocols are also often referred to as AAA servers. Let’s explore their applicability, along with pros and cons, in brief below:
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, or RADIUS, is a widely used AAA protocol. RADIUS is popular among Internet Service Providers and traditional corporate LANs and WANs. RADIUS is based on the UDP protocol and is best suited for network access.
Pros:
- Widely supported. RADIUS is a safe bet to integrate and centralize access control over network devices from different vendors.
- Simple enough for many network access use cases.
Cons:
- Lacks packet encryption. Only passwords are encrypted in access-request packets.
- Unreliable as the protocol is based on UDP. UDP may also affect accounting functionality because packet loss without retransmission functionality means permanent loss of the accounting data.
- The authentication and authorization processes are combined, making it harder to implement granular authorization.
TACACS+
Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus, or TACACS+, is one of the most capable and flexible AAA protocols and offers security benefits over RADIUS — such as packet encryption — and supports a wider range of extensibility. TACACS+ was initially developed by Cisco and eventually released to the open domain. But being a proprietary protocol, it is not as widely supported outside the Cisco networking ecosystem with buy-in from only a few other vendors such as Juniper Networks.
Pros:
- Reliable connection based on TCP.
- Support for privilege management in configuration commands means TACACS+ is best suited for device administration.
- Supports encrypted packet transmission.
- Separation of authentication, authorization, and accounting features makes integrating with external authentication, authorization, or accounting systems easy.
Cons:
- Proprietary and not widely supported outside the Cisco ecosystem.
Diameter
Diameter is a AAA protocol developed to supersede the RADIUS protocol. In fact, the name Diameter is derived from RADIUS as “diameter is twice the radius”. Diameter supports modern network access requirements over LTE networks and mobile devices.
Pros:
- Reliable connection (supports TCP and SCTP) and has built-in failover mechanism.
- Supports TLS.
- Roaming support via proxy chaining.
- Support for access control over LTE networks.
- Capability negotiation between client and servers.
Cons:
- Not as popular and widely supported as RADIUS and TACACS+.
AAA protocols vs. authentication protocols
There are widely used network authentication protocols that are often confused with AAA protocols. These authentication protocols include Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP), Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), Kerberos, etc. Although authentication protocols are popular amongst Point-To-Point (PPP) protocols, many modern authentication protocols share or derive schemes from these authentication protocols.
In contrast to AAA protocols, authentication protocols only focus on providing an authentication mechanisms to clients and servers. They can even be used as an authentication method for AAA protocols.
AAA protocols vs. directory services
It is challenging to catalog network resources and their relationship with users, machines and services in a computer network. Directory services allow an easy catalog of this information that helps to implement authentication and authorization in a corporate network structurally. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is the most widely used protocol for directory services, and OpenLDAP and Microsoft Active Directory are popular LDAP-based services.
AAA servers can use LDAP servers to store users and network resource data that can be utilized for authentication and authorization information.
Teleport cybersecurity blog posts and tech news
Every other week we'll send a newsletter with the latest cybersecurity news and Teleport updates.
Conclusion
Authentication, authorization, accounting, or AAA protocols, centralize access controls for network access and network device administration. The widely used AAA protocols include RADIUS, TACACS+, and DIAMETER, and they support a wide range of authentication and authorization protocols to extend security functionality. While these AAA protocols offer standardized access control, they lack support for modern secure components and fall short in modern heterogeneous networks that comprise many different network services. Thus, these AAA protocols are rarely seen in modern infrastructure access management.
Modern AAA server for network access
Although the concept of AAA protocols remains the same, traditional AAA protocols and servers are most suitable for access control in a traditional, static infrastructure environment. Modern network services are software-defined and mostly communicate over TLS. They are mutually authenticated with certificates and defer authentication, authorization and accounting to external purpose-built solutions for scalability and better security.
Teleport is a modern, open-source replacement for traditional AAA servers and supports certificate-based authentication, RBAC authorization, and deep protocol-level accounting and auditing functionality. Teleport is open source and built with open standards. Learn how Teleport brings AAA to modern infrastructure network access. You can download the community edition to try it for yourself.
Tags
Teleport Newsletter
Stay up-to-date with the newest Teleport releases by subscribing to our monthly updates.

Subscribe to our newsletter

