Run the Jira Access Request Plugin
This guide explains how to set up the Teleport Access Request plugin for Jira. Teleport's Jira integration allows you to manage Teleport Access Requests as Jira issues.
The Teleport Jira plugin synchronizes a Jira project board with the Access Requests processed by your Teleport cluster. When you change the status of an Access Request within Teleport, the plugin updates the board. And when you update the status of an Access Request on the board, the plugin notifies a Jira webhook run by the plugin, which modifies the Access Request in Teleport.
This integration is hosted on Teleport Cloud
In Teleport Enterprise Cloud, Teleport manages the Mattermost integration for you, and you can enroll the Mattermost integration from the Teleport Web UI.
Visit the Teleport Web UI and click Access Management on the menu bar at the top of the screen.
On the left sidebar, click Enroll New Integration to visit the "Enroll New Integration" page:
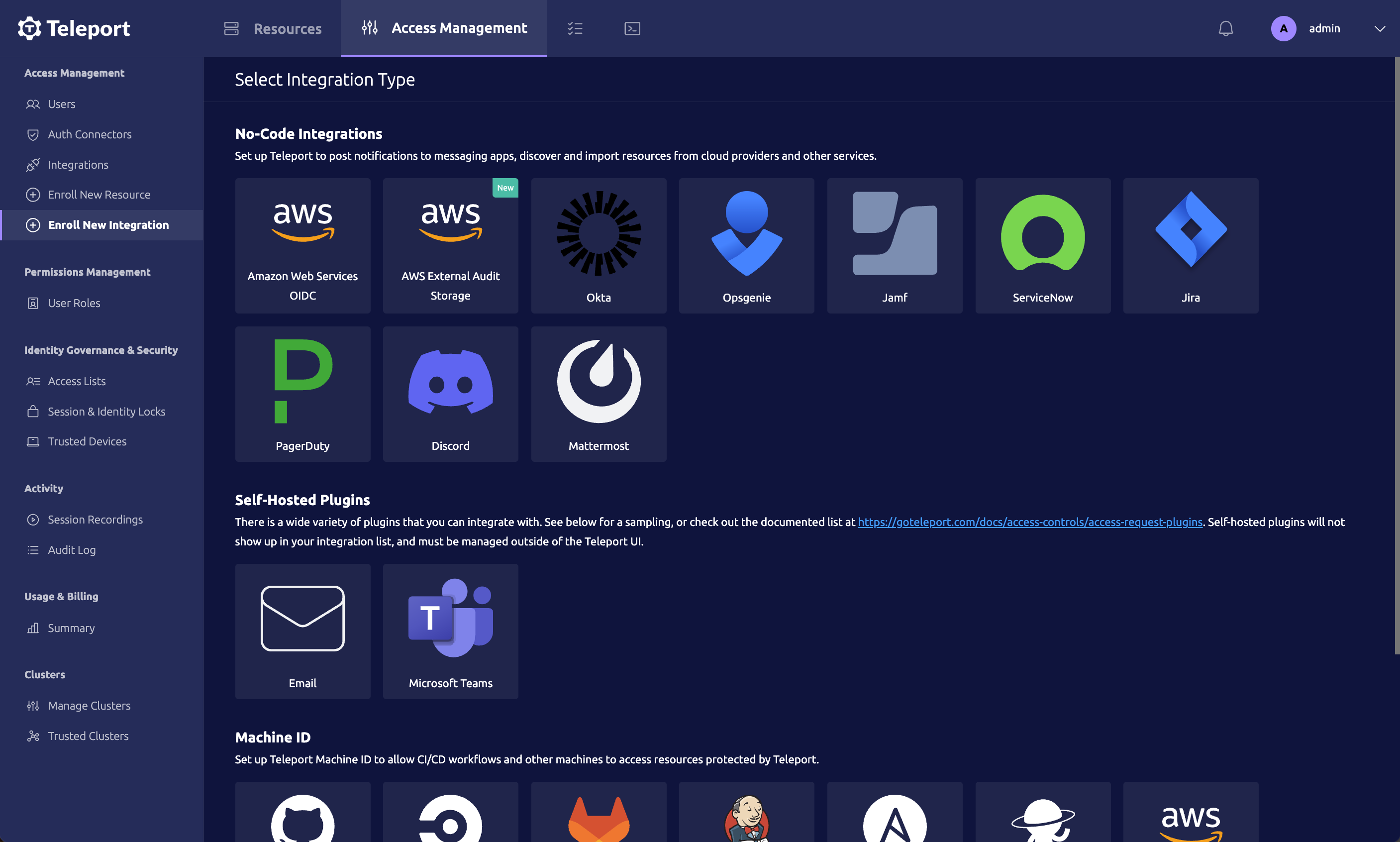
On the "Select Integration Type" menu, click the tile for your integration. You will see a page with instructions to set up the integration, as well as a form that you can use to configure the integration.
Prerequisites
-
A running Teleport cluster. If you want to get started with Teleport, sign up for a free trial.
-
The Enterprise
tctladmin tool andtshclient tool version >= 15.4.22, which you can download from your Teleport account workspace or the Teleport Installation Downloads page.
Recommended: Configure Machine ID to provide short-lived Teleport
credentials to the plugin. Before following this guide, follow a Machine ID
deployment guide
to run the tbot binary on your infrastructure.
-
A Jira account with permissions to create applications and webhooks.
-
A registered domain name for the Jira webhook. Jira notifies the webhook of changes in your project board.
-
An environment where you will run the Jira plugin. This is either:
- A Linux virtual machine with ports
80and8081open, plus a means of accessing the host (e.g., OpenSSH with an SSH port exposed to your workstation). - A Kubernetes cluster deployed via a cloud provider. This guide shows you how
to allow traffic to the Jira plugin via a
LoadBalancerservice, so your environment must support services of this type.
- A Linux virtual machine with ports
-
A means of providing TLS credentials for the Jira webhook run by the plugin. TLS certificates must not be self signed. For example, you can obtain TLS credentials for the webhook with Let's Encrypt by using an ACME client.
- If you run the plugin on a Linux server, you must provide TLS credentials to a directory available to the plugin.
- If you run the plugin on Kubernetes, you must write these credentials to a
secret that the plugin can read. This guide assumes that the name of the
secret is
teleport-plugin-jira-tls.
-
To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials.tctlis supported on macOS and Linux machines.For example:
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com [email protected]
$ tctl status
# Cluster teleport.example.com
# Version 15.4.22
# CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678If you can connect to the cluster and run the
tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions.
Step 1/7. Define RBAC resources
Enable Role Access Requests
Before you set up the Jira plugin, you need to enable Role Access Requests in your Teleport cluster.
For the purpose of this guide, we will define an editor-requester role, which
can request the built-in editor role, and an editor-reviewer role that can
review requests for the editor role.
Create a file called editor-request-rbac.yaml with the following content:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: editor-reviewer
spec:
allow:
review_requests:
roles: ['editor']
---
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: editor-requester
spec:
allow:
request:
roles: ['editor']
thresholds:
- approve: 1
deny: 1
Create the roles you defined:
$ tctl create -f editor-request-rbac.yaml
role 'editor-reviewer' has been created
role 'editor-requester' has been created
Allow yourself to review requests by users with the editor-requester role by
assigning yourself the editor-reviewer role.
Assign the editor-reviewer role to your Teleport user by running the appropriate
commands for your authentication provider:
- Local User
- GitHub
- SAML
- OIDC
-
Retrieve your local user's roles as a comma-separated list:
$ ROLES=$(tsh status -f json | jq -r '.active.roles | join(",")') -
Edit your local user to add the new role:
$ tctl users update $(tsh status -f json | jq -r '.active.username') \
--set-roles "${ROLES?},editor-reviewer" -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
githubauthentication connector:$ tctl get github/github --with-secrets > github.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto thegithub.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the github.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
github.yaml, addingeditor-reviewerto theteams_to_rolessection.The team you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the team must include your user account and should be the smallest team possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
teams_to_roles:
- organization: octocats
team: admins
roles:
- access
+ - editor-reviewer -
Apply your changes:
$ tctl create -f github.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
samlconfiguration resource:$ tctl get --with-secrets saml/mysaml > saml.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto thesaml.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the saml.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
saml.yaml, addingeditor-reviewerto theattributes_to_rolessection.The attribute you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the group must include your user account and should be the smallest group possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
attributes_to_roles:
- name: "groups"
value: "my-group"
roles:
- access
+ - editor-reviewer -
Apply your changes:
$ tctl create -f saml.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
-
Retrieve your
oidcconfiguration resource:$ tctl get oidc/myoidc --with-secrets > oidc.yamlNote that the
--with-secretsflag adds the value ofspec.signing_key_pair.private_keyto theoidc.yamlfile. Because this key contains a sensitive value, you should remove the oidc.yaml file immediately after updating the resource. -
Edit
oidc.yaml, addingeditor-reviewerto theclaims_to_rolessection.The claim you should map to this role depends on how you have designed your organization's role-based access controls (RBAC). However, the group must include your user account and should be the smallest group possible within your organization.
Here is an example:
claims_to_roles:
- name: "groups"
value: "my-group"
roles:
- access
+ - editor-reviewer -
Apply your changes:
$ tctl create -f oidc.yaml -
Sign out of the Teleport cluster and sign in again to assume the new role.
Create a user called myuser who has the editor-requester role. This user
cannot edit your cluster configuration unless they request the editor role:
$ tctl users add myuser --roles=editor-requester
tctl will print an invitation URL to your terminal. Visit the URL and log in
as myuser for the first time, registering credentials as configured for your
Teleport cluster.
Later in this guide, you will have myuser request the editor role so you can
review the request using the Teleport plugin.
Create a user and role for the plugin
Teleport's Access Request plugins authenticate to your Teleport cluster as a user with permissions to list, read, and update Access Requests. This way, plugins can retrieve Access Requests from the Teleport Auth Service, present them to reviewers, and modify them after a review.
Define a user and role called access-plugin by adding the following content to
a file called access-plugin.yaml:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: access-plugin
spec:
allow:
rules:
- resources: ['access_request']
verbs: ['list', 'read', 'update']
- resources: ['access_plugin_data']
verbs: ['update']
---
kind: user
metadata:
name: access-plugin
spec:
roles: ['access-plugin']
version: v2
Create the user and role:
$ tctl create -f access-plugin.yaml
As with all Teleport users, the Teleport Auth Service authenticates the
access-plugin user by issuing short-lived TLS credentials. In this case, we
will need to request the credentials manually by impersonating the
access-plugin role and user.
If you are running a self-hosted Teleport Enterprise deployment and are using
tctl from the Auth Service host, you will already have impersonation
privileges.
To grant your user impersonation privileges for access-plugin, define a role
called access-plugin-impersonator by pasting the following YAML document into
a file called access-plugin-impersonator.yaml:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: access-plugin-impersonator
spec:
allow:
impersonate:
roles:
- access-plugin
users:
- access-plugin
Create the access-plugin-impersonator role:
$ tctl create -f access-plugin-impersonator.yaml
Retrieve your user definition:
$ TELEPORT_USER=$(tsh status --format=json | jq -r .active.username)
$ tctl get users/${TELEPORT_USER?} > myuser.yaml
Edit myuser.yaml to include the role you just created:
roles:
- access
- auditor
- editor
+ - access-plugin-impersonator
Apply your changes:
$ tctl create -f myuser.yaml
Log out of your Teleport cluster and log in again. You will now be able to
generate signed certificates for the access-plugin role and user.
Step 2/7. Install the Teleport Jira plugin
Install the Teleport Jira plugin following the instructions below, which depend on whether you are deploying the plugin on a host (e.g., an EC2 instance) or a Kubernetes cluster.
The Teleport Jira plugin must run on a host or Kubernetes cluster that can access both Jira and your Teleport Proxy Service (or Teleport Enterprise Cloud tenant).
- Download
- Docker Image
- From Source
- Helm Chart
We currently only provide linux-amd64 binaries. You can also compile these
plugins from source. You can run the plugin from a remote host or your local
development machine.
$ curl -L -O https://get.gravitational.com/teleport-access-jira-v15.4.22-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz
$ tar -xzf teleport-access-jira-v15.4.22-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz
$ cd teleport-access-jira
$ sudo ./install
Make sure the binary is installed:
$ teleport-jira version
teleport-jira v15.4.22 git:teleport-jira-v15.4.22-fffffffff go1.21
We currently only provide Docker images for linux-amd64.
Pull the Docker image for the latest access request plugin by running the following command:
$ docker pull public.ecr.aws/gravitational/teleport-plugin-jira:15.4.22
Make sure the plugin is installed by running the following command:
$ docker run public.ecr.aws/gravitational/teleport-plugin-jira:15.4.22 version
teleport-jira v15.4.22 git:teleport-jira-v15.4.22-api/14.0.0-gd1e081e 1.21
For a list of available tags, visit Amazon ECR Public Gallery.
To install from source you need git and go installed. If you do not have Go
installed, visit the Go downloads page.
$ git clone https://github.com/gravitational/teleport -b branch/v15
$ cd teleport/integrations/access/jira
$ git checkout 15.4.22
$ make
Move the teleport-jira binary into your PATH.
Make sure the binary is installed:
$ teleport-jira version
teleport-jira v15.4.22 git:teleport-jira-v15.4.22-fffffffff go1.21
Allow Helm to install charts that are hosted in the Teleport Helm repository:
$ helm repo add teleport https://charts.releases.teleport.dev
Update the cache of charts from the remote repository:
$ helm repo update
Step 3/7. Export the access plugin identity
Give the plugin access to a Teleport identity file. We recommend using Machine
ID for this in order to produce short-lived identity files that are less
susceptible to exfiltration, though in demo deployments, you can generate
longer-lived identity files with tctl:
- Machine ID
- Long-lived identity files
Configure tbot with an output that will produce the credentials needed by
the plugin. As the plugin will be accessing the Teleport API, the correct
output type to use is identity.
For this guide, the directory destination will be used. This will write these
credentials to a specified directory on disk. Ensure that this directory can
be written to by the Linux user that tbot runs as, and that it can be read by
the Linux user that the plugin will run as.
Modify your tbot configuration to add an identity output.
If running tbot on a Linux server, use the directory output to write
identity files to the /opt/machine-id directory:
outputs:
- type: identity
destination:
type: directory
# For this guide, /opt/machine-id is used as the destination directory.
# You may wish to customize this. Multiple outputs cannot share the same
# destination.
path: /opt/machine-id
If running tbot on Kubernetes, write the identity file to Kubernetes secret
instead:
outputs:
- type: identity
destination:
type: kubernetes_secret
name: teleport-plugin-slack-identity
If operating tbot as a background service, restart it. If running tbot in
one-shot mode, execute it now.
You should now see an identity file under /opt/machine-id or a Kubernetes
secret named teleport-plugin-slack-identity. This contains the private key and signed
certificates needed by the plugin to authenticate with the Teleport Auth
Service.
Like all Teleport users, access-plugin needs signed credentials in order to
connect to your Teleport cluster. You will use the tctl auth sign command to
request these credentials.
The following tctl auth sign command impersonates the access-plugin user,
generates signed credentials, and writes an identity file to the local
directory:
$ tctl auth sign --user=access-plugin --out=identity
The plugin connects to the Teleport Auth Service's gRPC endpoint over TLS.
The identity file, identity, includes both TLS and SSH credentials. The
plugin uses the SSH credentials to connect to the Proxy Service, which
establishes a reverse tunnel connection to the Auth Service. The plugin
uses this reverse tunnel, along with your TLS credentials, to connect to the
Auth Service's gRPC endpoint.
Certificate Lifetime
By default, tctl auth sign produces certificates with a relatively short
lifetime. For production deployments, we suggest using Machine
ID to programmatically issue and renew
certificates for your plugin. See our Machine ID getting started
guide to learn more.
Note that you cannot issue certificates that are valid longer than your existing credentials.
For example, to issue certificates with a 1000-hour TTL, you must be logged in with a session that is
valid for at least 1000 hours. This means your user must have a role allowing
a max_session_ttl of at least 1000 hours (60000 minutes), and you must specify a --ttl
when logging in:
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --ttl=60060
If you are running the plugin on a Linux server, create a data directory to hold certificate files for the plugin:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/teleport/api-credentials
$ sudo mv identity /var/lib/teleport/plugins/api-credentials
If you are running the plugin on Kubernetes, Create a Kubernetes secret that contains the Teleport identity file:
$ kubectl -n teleport create secret generic --from-file=identity teleport-plugin-jira-identity
Once the Teleport credentials expire, you will need to renew them by running the
tctl auth sign command again.
Step 4/7. Set up a Jira project
In this section, you will create a Jira a project that the Teleport plugin can modify when a Teleport user creates or updates an Access Request. The plugin then uses the Jira webhook to monitor the state of the board and respond to any changes in the tickets it creates.
Create a project for managing Access Requests
In Jira, find the top navigation bar and click Projects -> Create project. Select Kanban for the template, then Use template. Click Select a company-managed project.
You'll see a screen where you can enter a name for your project. In this guide,
we assume that your project is called "Teleport Access Requests", which
receives the key TAR by default.
Make sure "Connect repositories, documents, and more" is unset, then click Create project.
In the three-dots menu on the upper right of your new board, click Board settings, then click Columns. Edit the statuses in your board so it contains the following four:
- Pending
- Approved
- Denied
- Expired
Create a column with the same name as each status. The result should be the following:
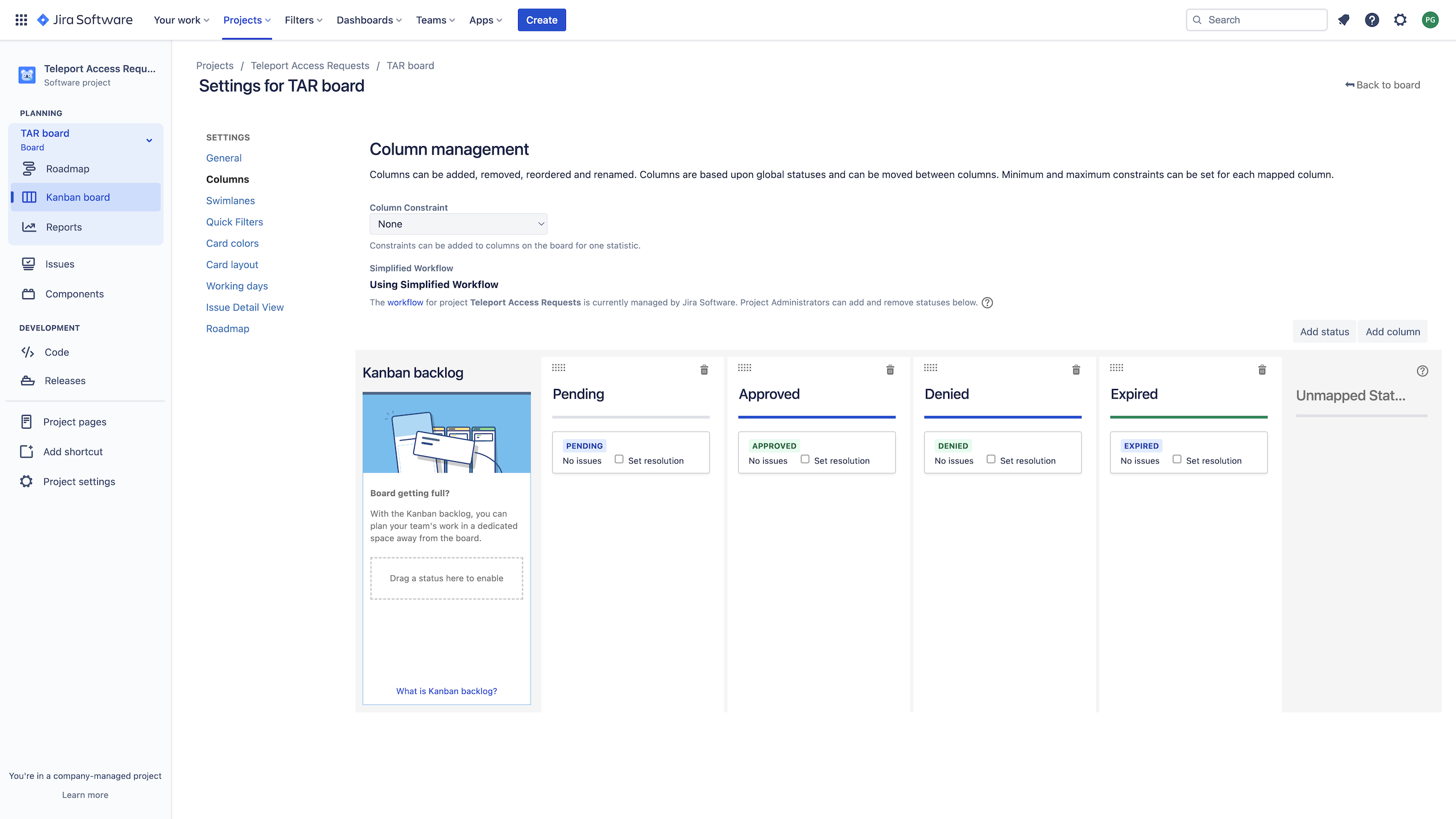
If your project board does not contain these (and only these) columns, each with a status of the same name, the Jira Access Request plugin will behave in unexpected ways. Remove all other columns and statuses.
Click Back to board to review your changes.
Set up a request ID field
The Teleport Jira plugin expects tasks in the Teleport Access Requests project
to include a field called teleportAccessRequestId, which it uses to track
individual Access Requests. This prevents users from tampering with or forging
Access Requests.
To set up the teleportAccessRequestId field, click Project settings on the
left navigation bar, then click Issues -> Fields.
In the Actions menu, click Edit fields. Click the Custom fields tab
in the left sidebar, then Create custom field. Add a Short Text field
named teleportAccessRequestId. Click the checkbox next to Default Screen
to associate that field with this screen. Click Update.
Next, add the custom field to your Teleport Access Requests project. Click
Projects > Teleport Access Requests (TAR), then Project settings.
Click Issues -> Types on the left sidebar, then click Task >
Fields. Find the dropdown menu called Select Field, then select the
teleportAccessRequestId field you added earlier.
Retrieve your Jira API token
Obtain an API token that the Teleport Access Request plugin uses to make changes to your Jira project. Click the gear menu at the upper right of the screen, then click Atlassian account settings. Click Security > Create and manage API tokens > Create API token.
Choose any label and click Copy. Paste the API token into a convenient location (e.g., a password manager or local text document) so you can use it later in this guide when you configure the Jira plugin.
Set up a Jira webhook
Now that you have generated an API key that the Teleport Jira plugin uses to manage your project, enable Jira to notify the Teleport Jira plugin when your project is updated by creating a webhook.
Return to Jira. Click the gear menu on the upper right of the screen. Click System > WebHooks > Create a WebHook.
- Executable
- Helm Chart
Enter "Teleport Access Request Plugin" in the "Name" field. In the "URL" field,
enter the domain name you created for the plugin earlier, plus port 8081.
Enter "Teleport Access Request Plugin" in the "Name" field. In the "URL" field,
enter the domain name you created for the plugin earlier, plus port 443.
The webhook needs to be notified only when an issue is created, updated, or deleted. You can leave all the other boxes empty.
Click Create.
Step 5/7. Configure the Jira Access Request plugin
Earlier, you retrieved credentials that the Jira plugin uses to connect to Teleport and the Jira API. You will now configure the plugin to use these credentials and run the Jira webhook at the address you configured earlier.
Create a configuration file
- Executable or Docker
- Helm chart
The Teleport Jira plugin uses a configuration file in TOML format. Generate a
boilerplate configuration by running the following command (the plugin will not run
unless the config file is in /etc/teleport-jira.toml):
$ teleport-jira configure | sudo tee /etc/teleport-jira.toml > /dev/null
This should result in a configuration file like the one below:
# Example Jira plugin configuration TOML file
[teleport]
# Proxy Service domain and HTTPS port
auth_server = "myinstance.teleport.sh:443"
# Teleport identity file location
identity = "/var/lib/teleport/plugins/jira/identity"
# Refresh identity file on a periodic basis.
refresh_identity = true
[jira]
url = "https://[my-jira].atlassian.net" # JIRA URL
username = "[email protected]" # JIRA username
api_token = "token" # JIRA API token
project = "TAR" # JIRA Project key
[http]
# URL on which webhook server is accessible externally, for example,
# [https://]teleport-jira.example.com
public_addr = "example.com"
https_key_file = "/var/lib/teleport/plugins/jira/server.key" # TLS private key
https_cert_file = "/var/lib/teleport/plugins/jira/server.crt" # TLS certificate
[log]
output = "stderr" # Logger output. Could be "stdout", "stderr" or "/var/lib/teleport/jira.log"
severity = "INFO" # Logger severity. Could be "INFO", "ERROR", "DEBUG" or "WARN".
The Helm chart for the Jira plugin uses a YAML values file to configure the
plugin. On your local workstation, create a file called
teleport-jira-helm.yaml based on the following example:
teleport:
# Teleport Proxy Service domain name and HTTPS port. If you are using Teleport
# Enterprise Cloud, this should be in the form "your-account.teleport.sh:443"
address: "teleport.example.com:443"
# Secret containing a Teleport identity document
identityFromSecret: teleport-plugin-jira-identity
# Path within the secret containing the identity file.
identitySecretPath: identity
jira:
url: "https://[my-jira].atlassian.net" # URL of the Jira instance
username: [email protected] # Email of the bot user
apiToken: token # Token of the bot user
project: TAR # Project where issues will be created
http:
publicAddress: https://jira-teleport.example.com/
# Secret containing the TLS certificate
tlsFromSecret: teleport-plugin-jira-tls
# tlsKeySecretPath: tls.key # Name of the key inside the secret
# tlsCertSecretPath: tls.crt # Name of the certificate inside the secret
log:
output: stderr # Logger output. Could be "stdout", "stderr" or "/var/lib/teleport/jira.log"
severity: INFO # Logger severity. Could be "INFO", "ERROR", "DEBUG" or "WARN".
serviceType: ClusterIP
Edit the configuration file
Open the configuration file created for the Teleport Jira plugin and update the following fields:
[teleport]
The Jira plugin uses this section to connect to your Teleport cluster:
- Executable or Docker
- Helm Chart
addr: Include the hostname and HTTPS port of your Teleport Proxy Service
or Teleport Enterprise Cloud account (e.g., teleport.example.com:443 or
mytenant.teleport.sh:443).
identity: Fill this in with the path to the identity file you exported
earlier.
client_key, client_crt, root_cas: Comment these out, since we
are not using them in this configuration.
address: Include the hostname and HTTPS port of your Teleport Proxy Service
or Teleport Enterprise Cloud tenant (e.g., teleport.example.com:443 or
mytenant.teleport.sh:443).
identitySecretName: Fill in the identitySecretName field with the name
of the Kubernetes secret you created earlier.
identitySecretPath: Fill in the identitySecretPath field with the path
of the identity file within the Kubernetes secret. If you have followed the
instructions above, this will be identity.
If you are providing credentials to the plugin using a tbot binary that runs
on a Linux server, make sure the value of identity is the same as the path of
the identity file you configured tbot to generate, /opt/machine-id/identity.
Configure the plugin to periodically reload the identity file, ensuring that it does not attempt to connect to the Teleport Auth Service with expired credentials.
Add the following to the teleport section of the configuration:
refresh_identity = true
- Executable
- Helm Chart
jira
url: The URL of your Jira tenant, e.g., https://[your-jira].atlassian.net.
username: The username you were logged in as when you created your API token.
api_token: The Jira API token you retrieved earlier.
project: The project key for your project, which in our case is TAR.
You can leave issue_type as Task or remove the field, as Task is the
default.
http
The [http] setting block describes how the plugin's webhook works.
listen_addr indicates the address that the plugin listens on, and defaults
to :8081. If you opened port 8081 on your plugin host as we recommended
earlier in the guide, you can leave this option unset.
public_addr is the public address of your webhook. This is the domain name you added to the DNS A record you created earlier.
https_key_file and https_cert_file correspond to the private key and certificate you obtained before following this guide. Use the following values, assigning example.com to the domain name you created for the plugin earlier:
-
https_key_file:
$ /var/teleport-jira/tls/certificates/acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org-directory/example.com/example.com.key -
https_cert_file:
$ /var/teleport-jira/tls/certificates/acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org-directory/example.com/example.com.crt
jira
url: The URL of your Jira tenant, e.g., https://[your-jira].atlassian.net.
username: The username you were logged in as when you created your API token.
apiToken: The API token you retrieved earlier.
project: The project key for your project, which in our case is TAR.
You can leave issueType as Task or remove the field, as Task is the
default.
http
The http setting block describes how the plugin's webhook works.
publicAddress: The public address of your webhook. This is the domain name you created for your webhook. (We will create a DNS record for this domain name later.)
tlsFromSecret: The name of a Kubernetes secret containing TLS credentials
for the webhook. Use teleport-plugin-jira-tls.
Step 6/7. Run the Jira plugin
After finishing your configuration, you can now run the plugin and test your Jira-based Access Request flow:
- Executable
- Helm Chart
Run the following on your Linux host:
$ sudo teleport-jira start
INFO Starting Teleport Jira Plugin 12.1.1: jira/app.go:112
INFO Plugin is ready jira/app.go:142
Install the Helm chart for the Teleport Jira plugin:
$ helm install teleport-plugin-jira teleport/teleport-plugin-jira \
--namespace teleport \
--values values.yaml \
--version 15.4.22
Create a DNS record that associates the webhook's domain name with the address of the load balancer created by the Jira plugin Helm chart.
See whether the load balancer has a domain name or IP address:
$ kubectl -n teleport get services/teleport-plugin-jira
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
teleport-plugin-jira LoadBalancer 10.100.135.75 abc123.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30625/TCP,443:31672/TCP 134m
If the EXTERNAL-IP field has a domain name for the value, create a CNAME
record in which the domain name for your webhook points to the domain name of
the load balancer.
If the EXTERNAL-IP field's value is an IP address, create a DNS A record
instead.
You can then generate signed TLS credentials for the Jira plugin, which expects them to be written to a Kubernetes secret.
Check the status of the webhook
Confirm that the Jira webhook has started serving by sending a GET request to
the /status endpoint. If the webhook is running, it will return a 200 status
code with no document body:
- Executable
- Helm Chart
$ curl -v https://example.com:8081/status 2>&1 | grep "^< HTTP/2"
< HTTP/2 200
$ curl -v https://example.com:443/status 2>&1 | grep "^< HTTP/2"
< HTTP/2 200
Create an Access Request
Sign in to your cluster as the myuser user you created earlier and create an
Access Request:
- As an Admin
- As a User
- From the Web UI
A Teleport admin can create an Access Request for another user with tctl:
$ tctl request create myuser --roles=editor
Users can use tsh to create an Access Request and log in with approved roles:
$ tsh request create --roles=editor
Seeking request approval... (id: 8f77d2d1-2bbf-4031-a300-58926237a807)
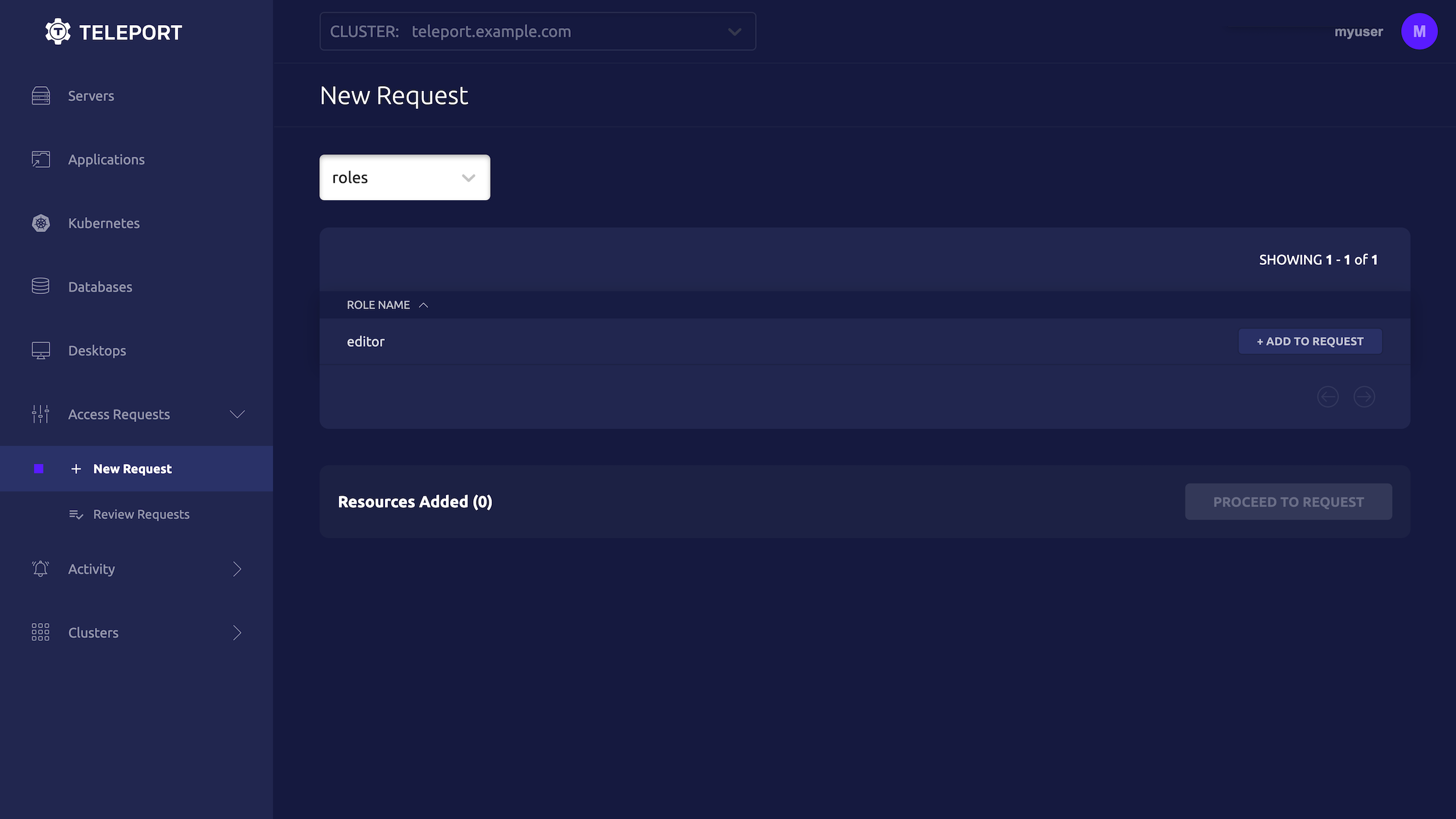
Users can request access using the Web UI by visiting the "Access Requests" tab and clicking "New Request":
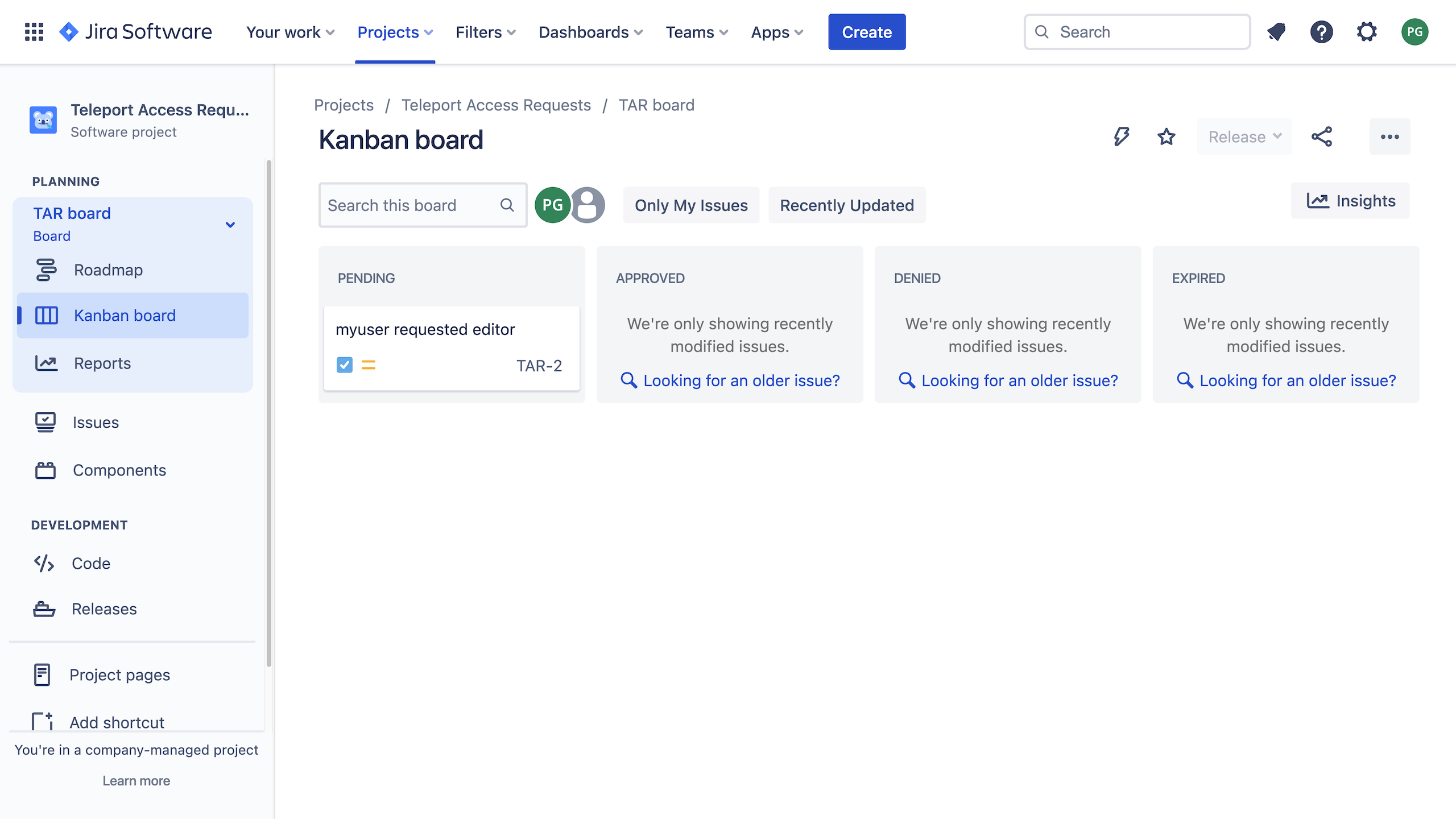
When you create the request, you will see a new task in the "Pending" column of the Teleport Access Requests board:
Resolve the request
Move the card corresponding to your new Access Request to the "Denied" column, then click the card and navigate to Teleport. You will see that the Access Request has been denied.
Anyone with access to the Jira project board can modify the status of Access Requests reflected on the board. You can check the Teleport audit log to ensure that the right users are reviewing the right requests.
When auditing Access Request reviews, check for events with the type Access Request Reviewed in the Teleport Web UI.
Step 7/7. Set up systemd
This step is only applicable if you are running the Teleport Jira plugin on a Linux machine.
In production, we recommend starting the Teleport plugin daemon via an init system like systemd. Here's the recommended Teleport plugin service unit file for systemd:
[Unit]
Description=Teleport Jira Plugin
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/teleport-jira start --config=/etc/teleport-jira.toml
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
PIDFile=/run/teleport-jira.pid
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save this as teleport-jira.service or another unit file load
path
supported by systemd.
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport-jira
$ sudo systemctl start teleport-jira